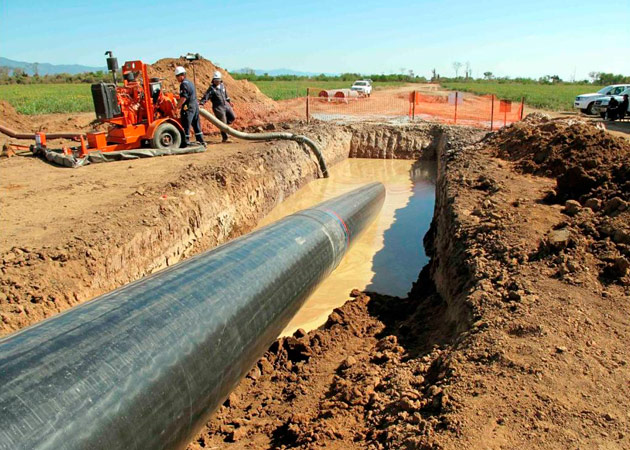
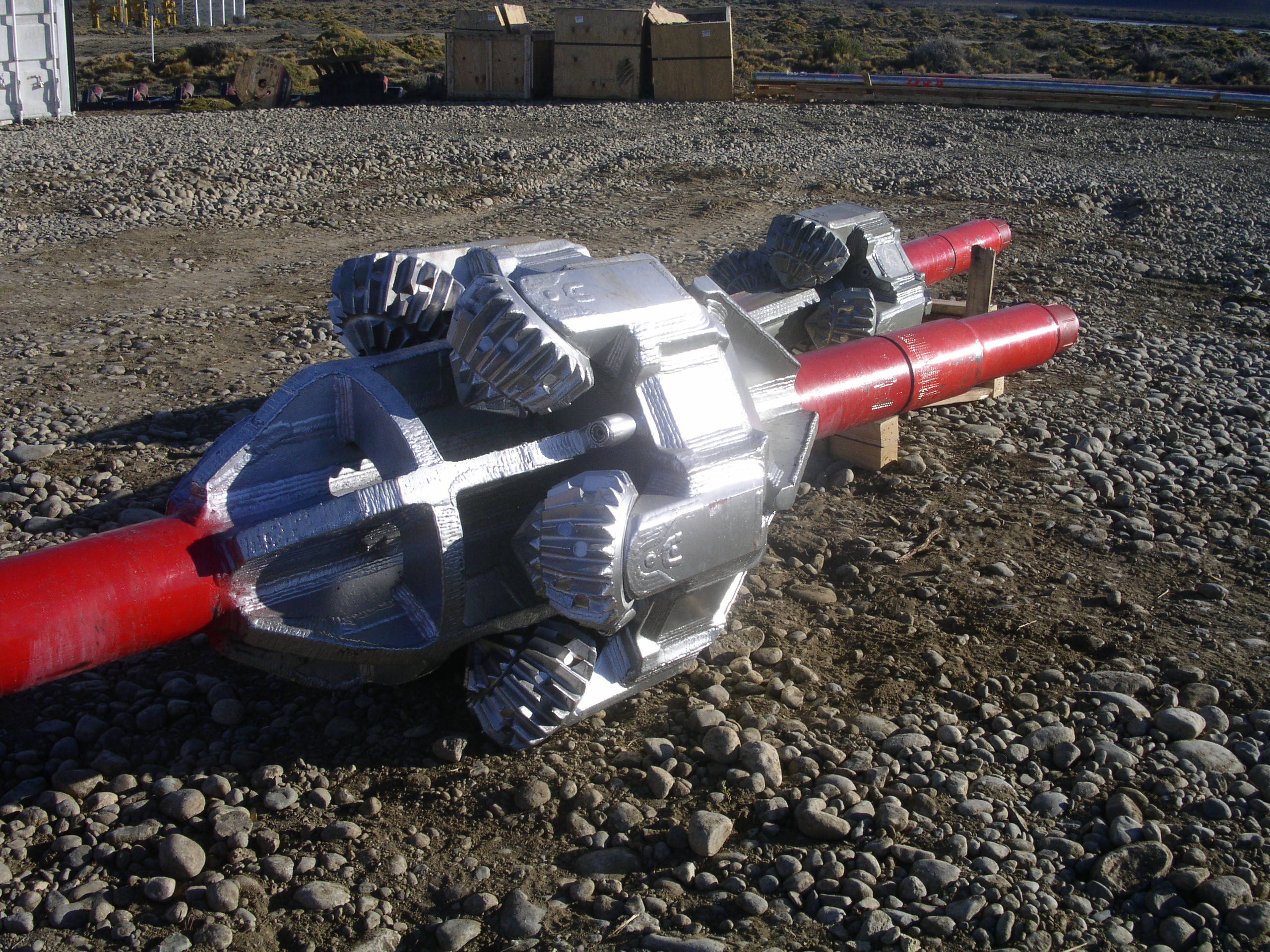
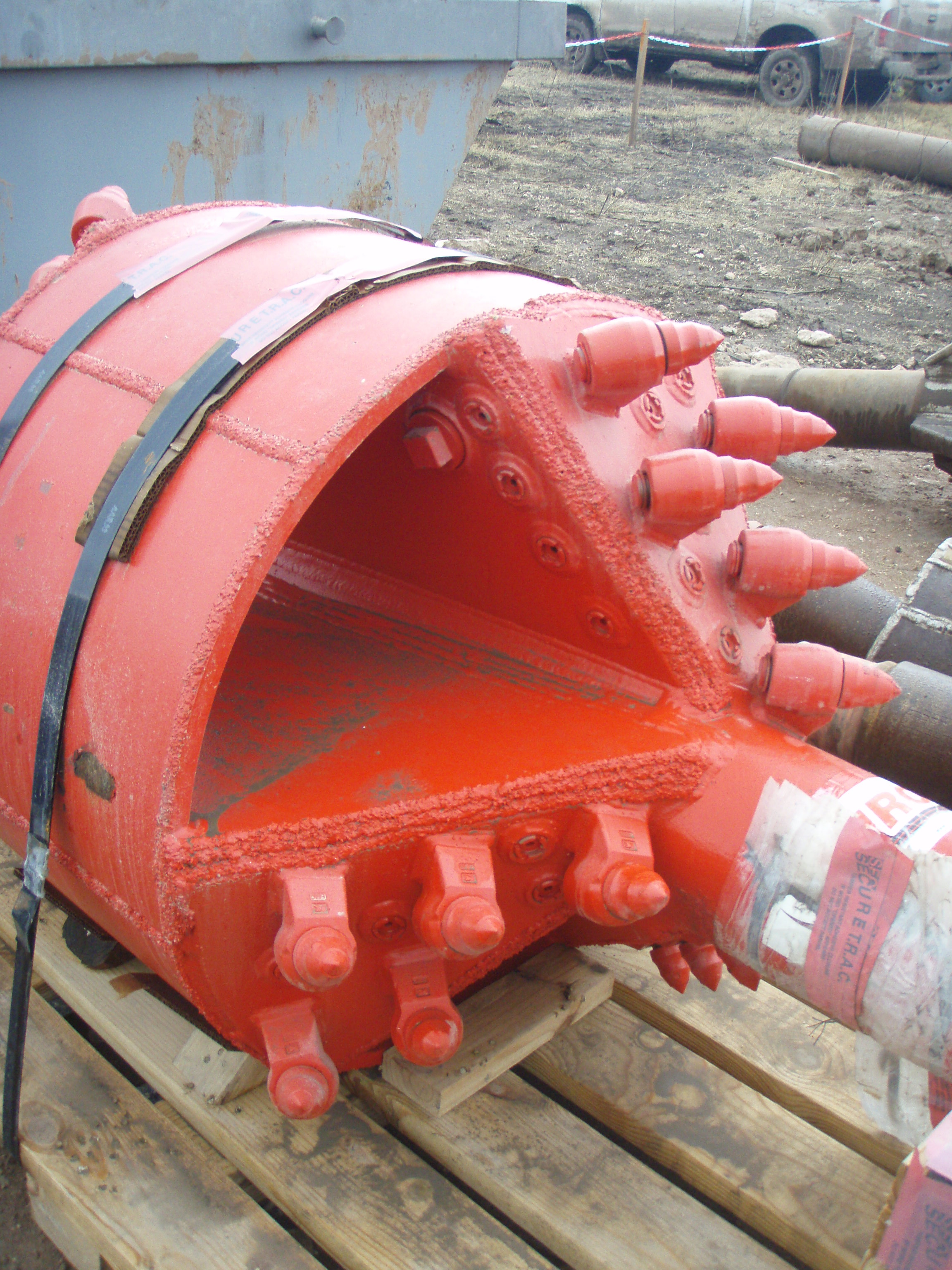
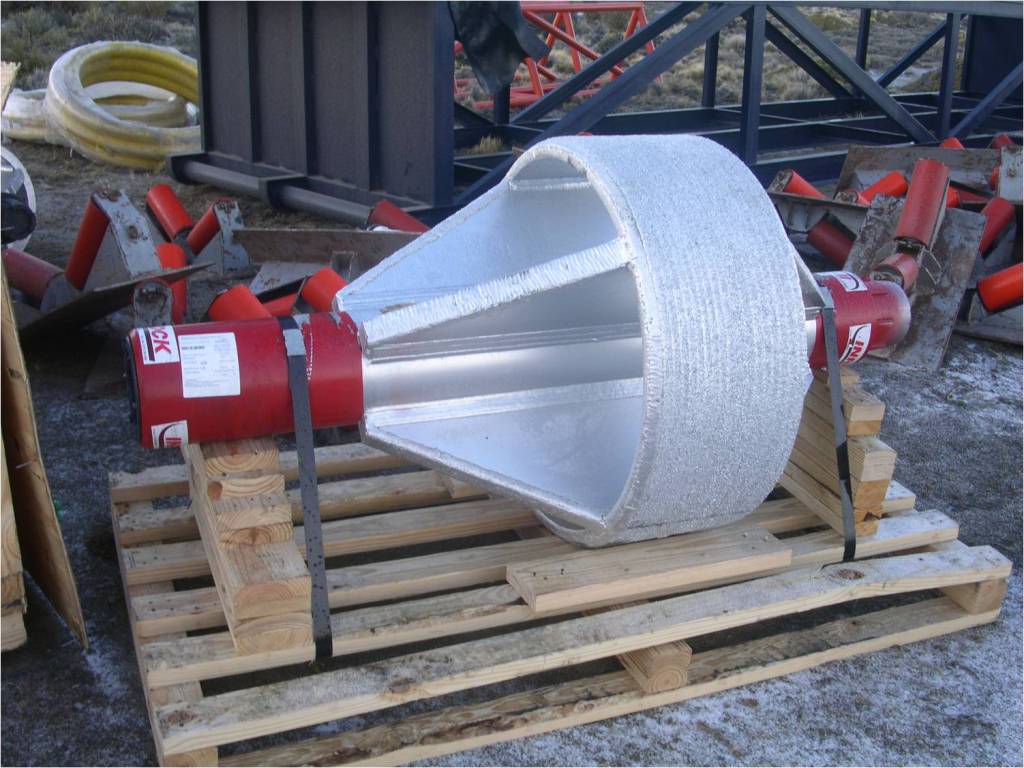
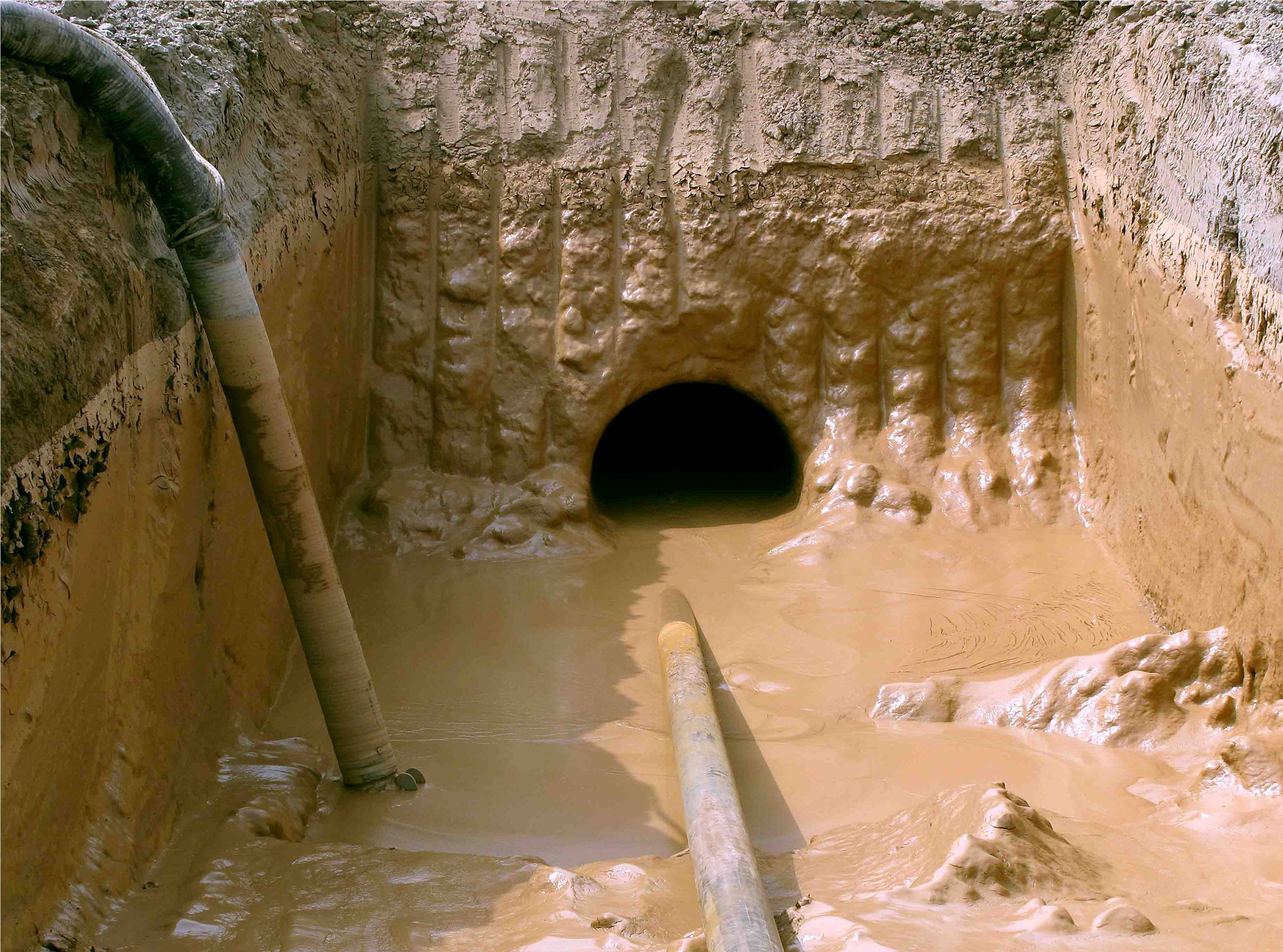
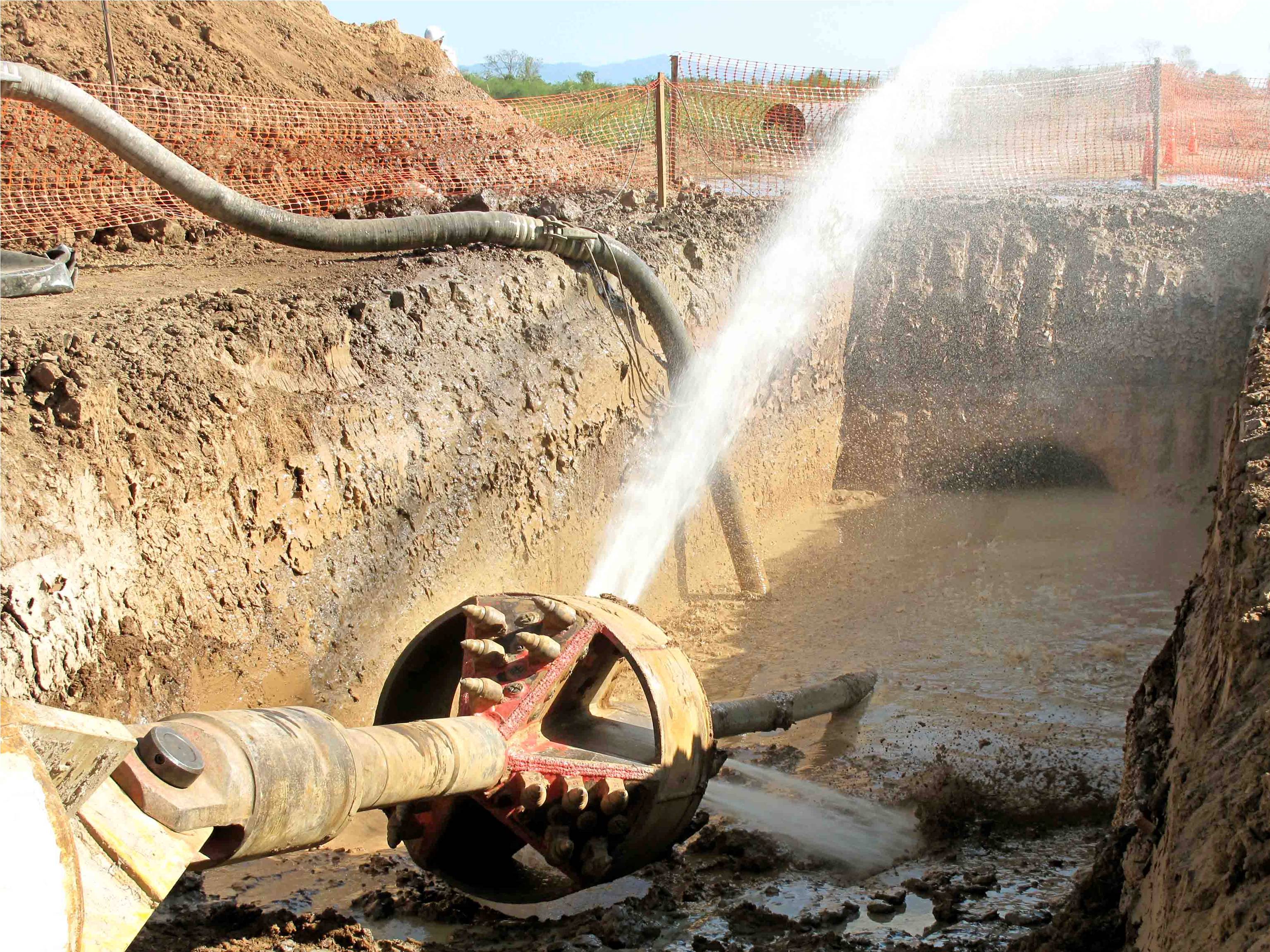
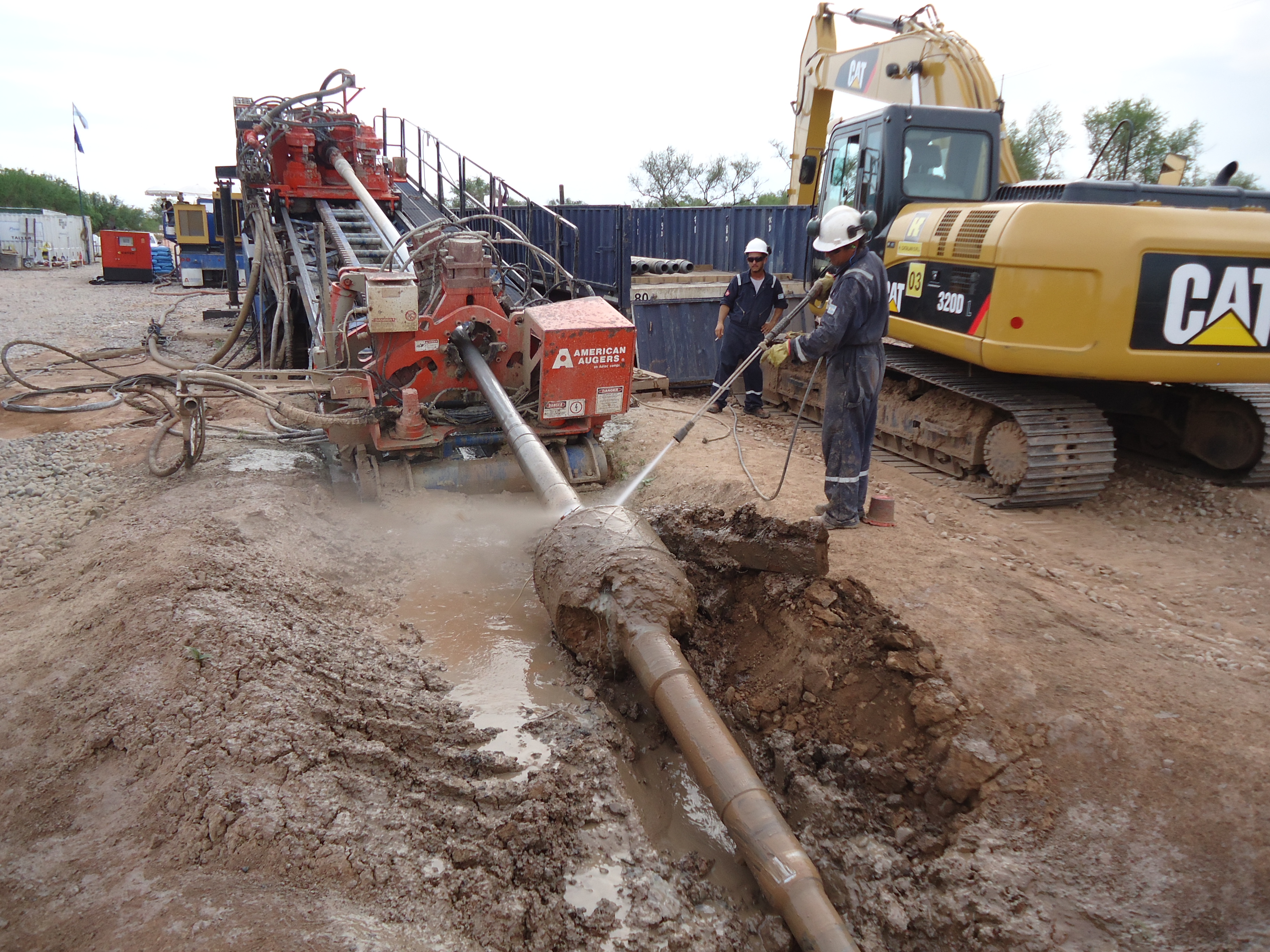
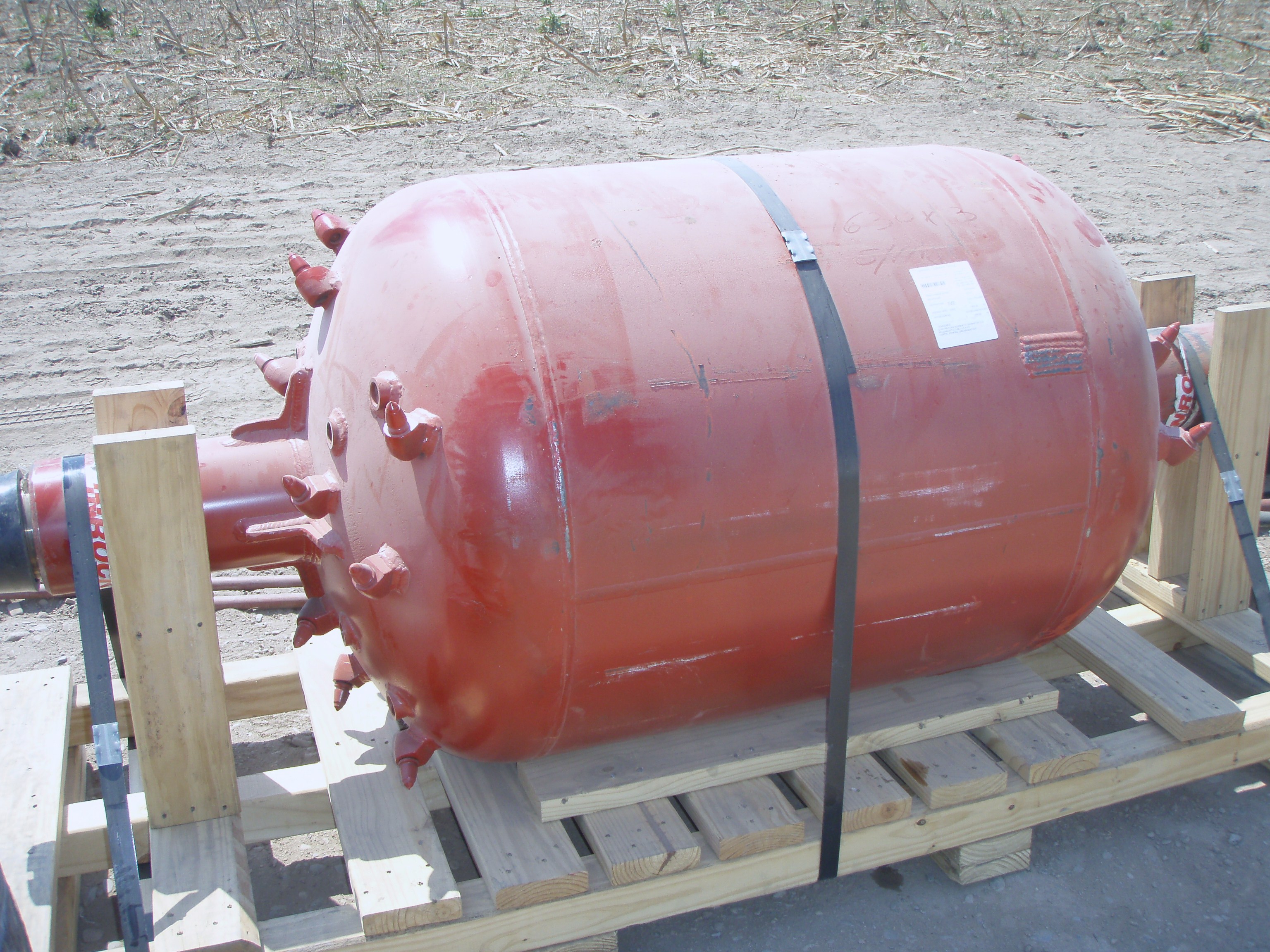
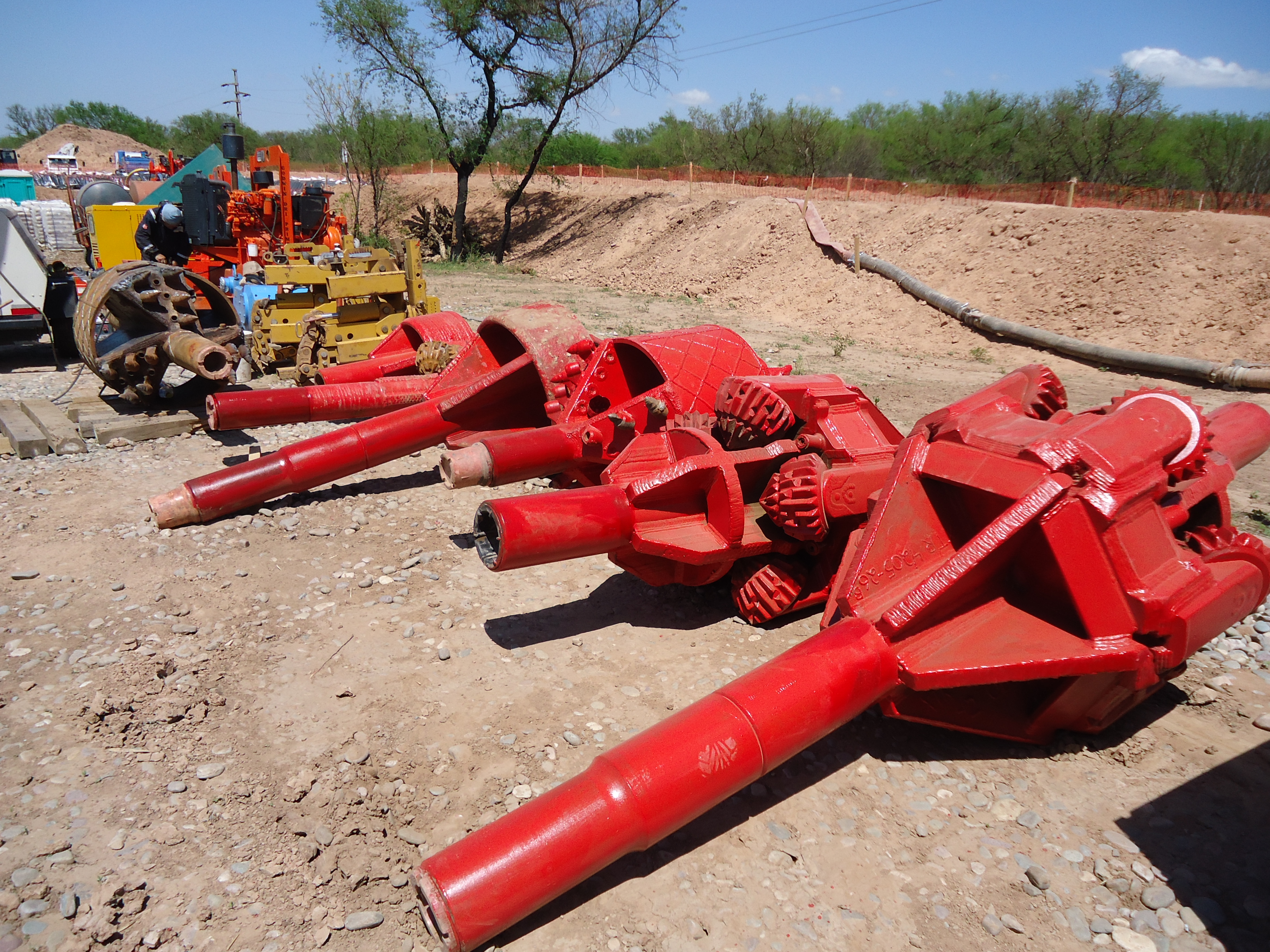
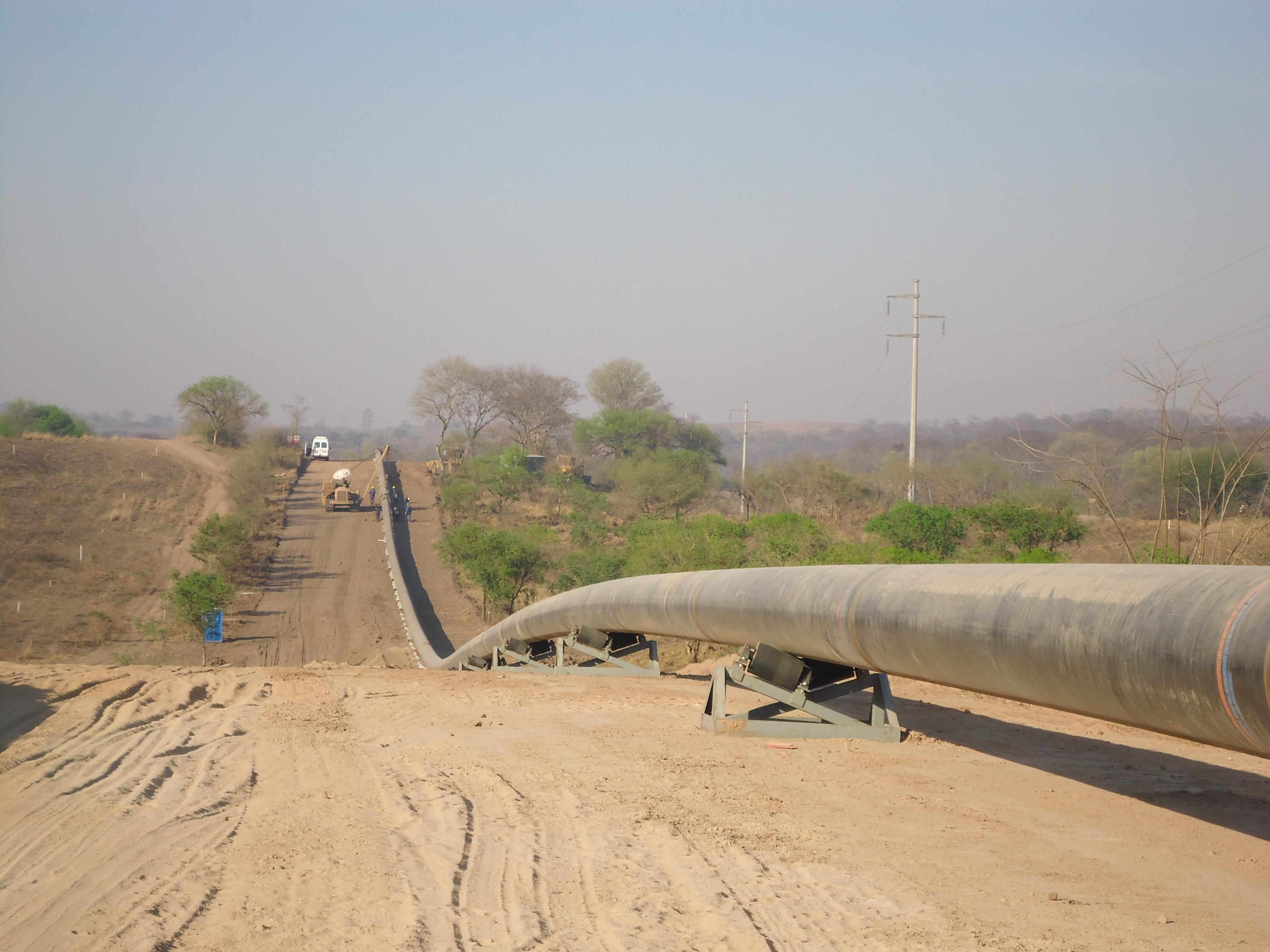
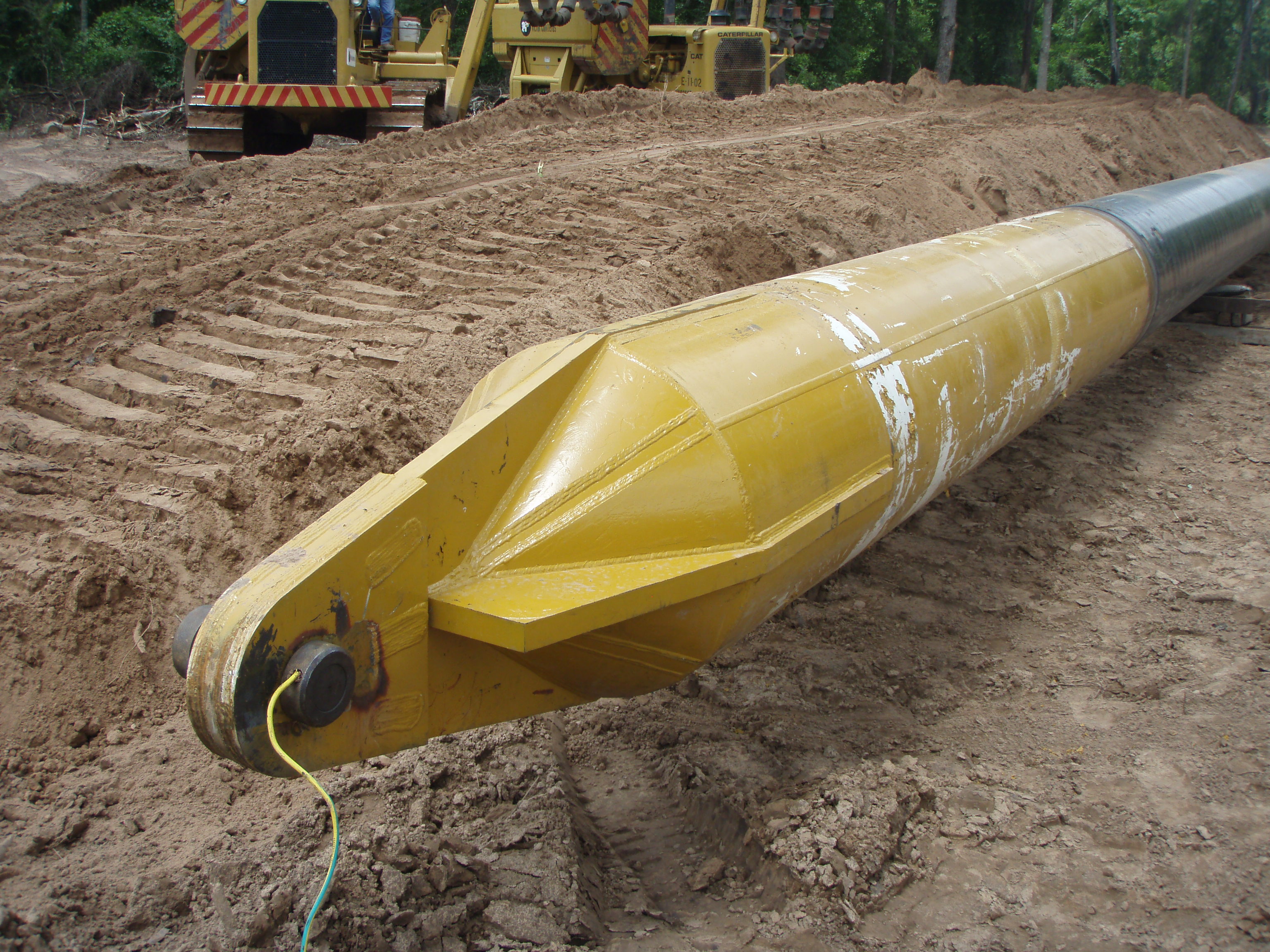
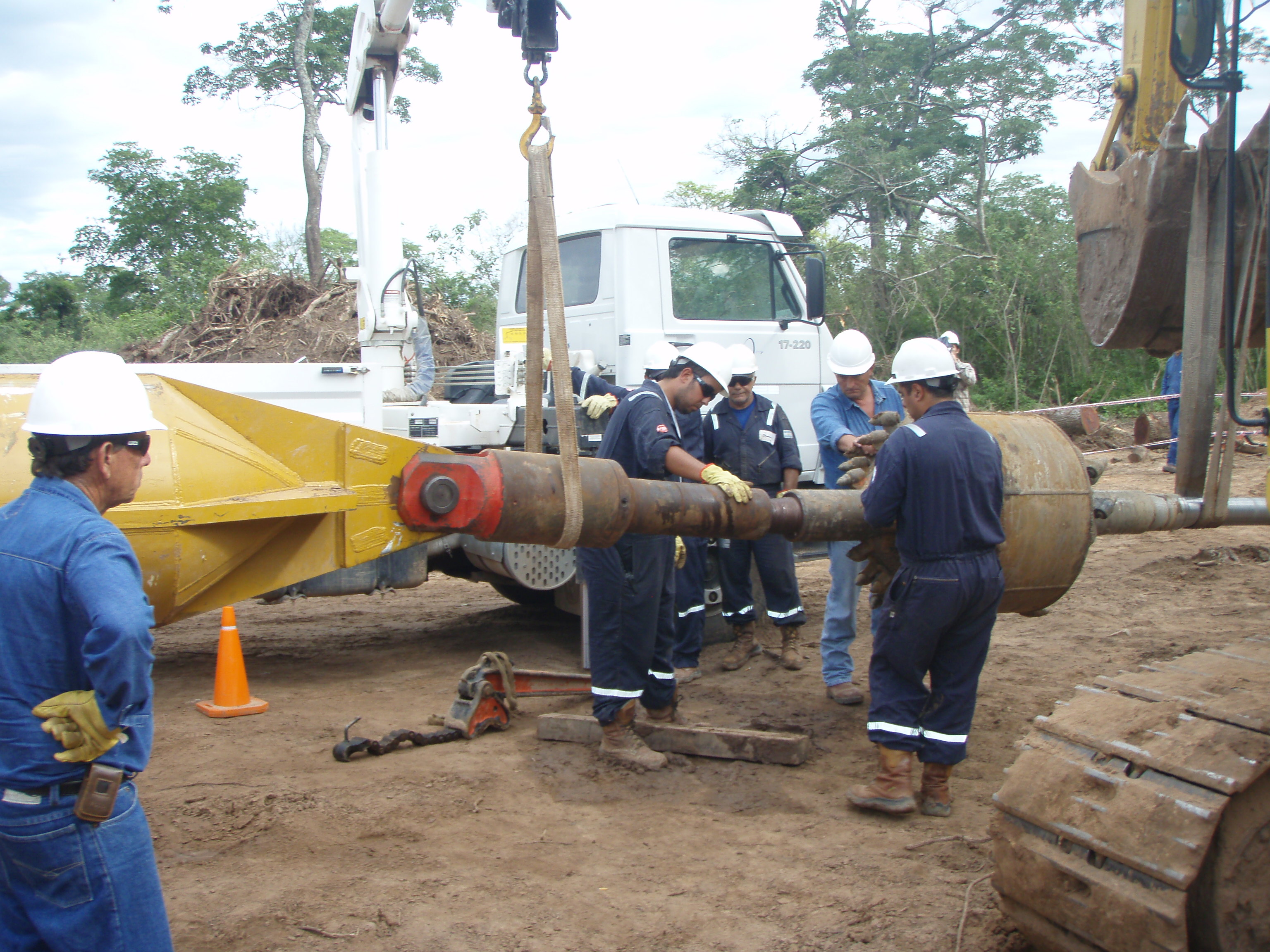
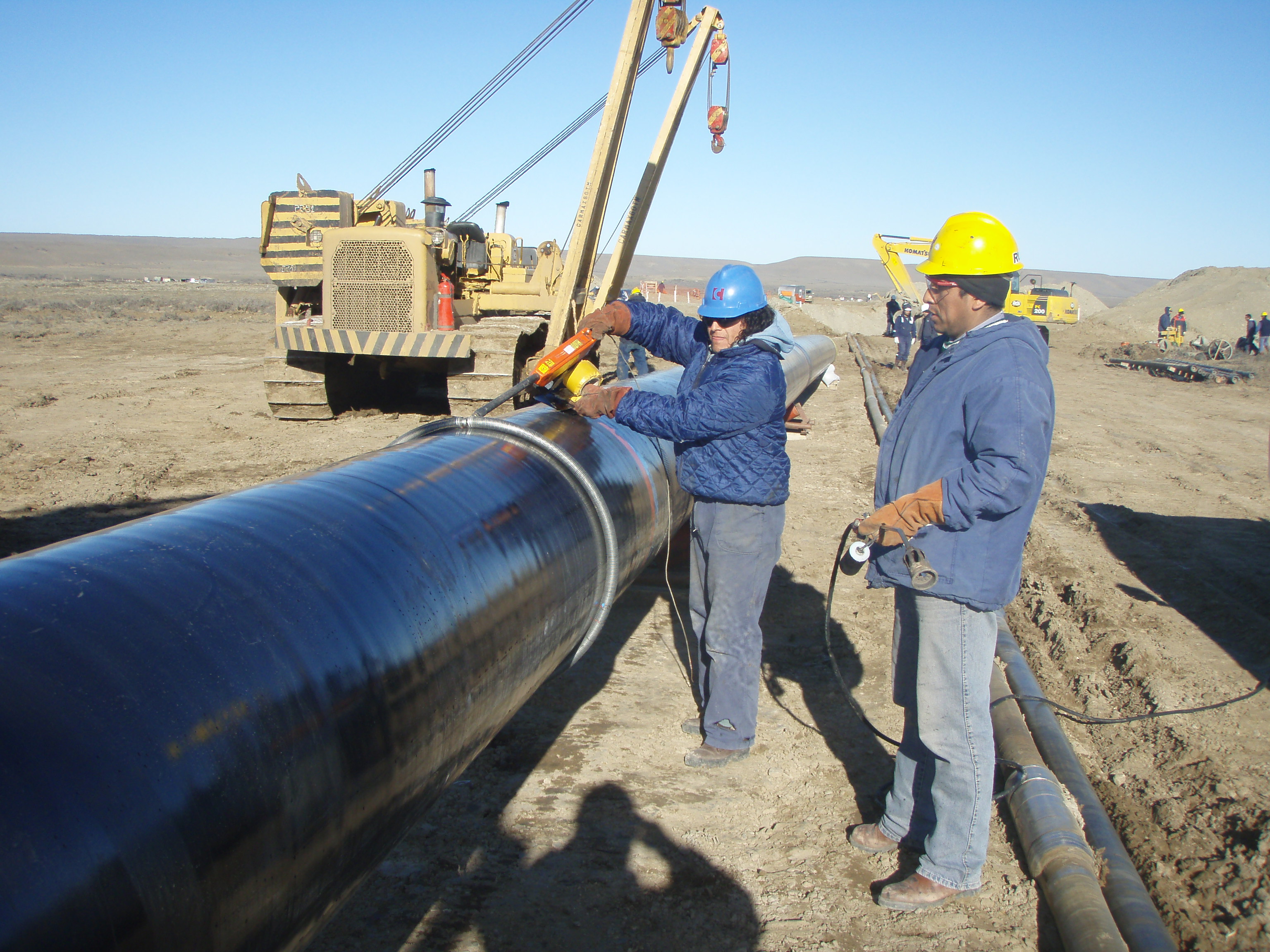
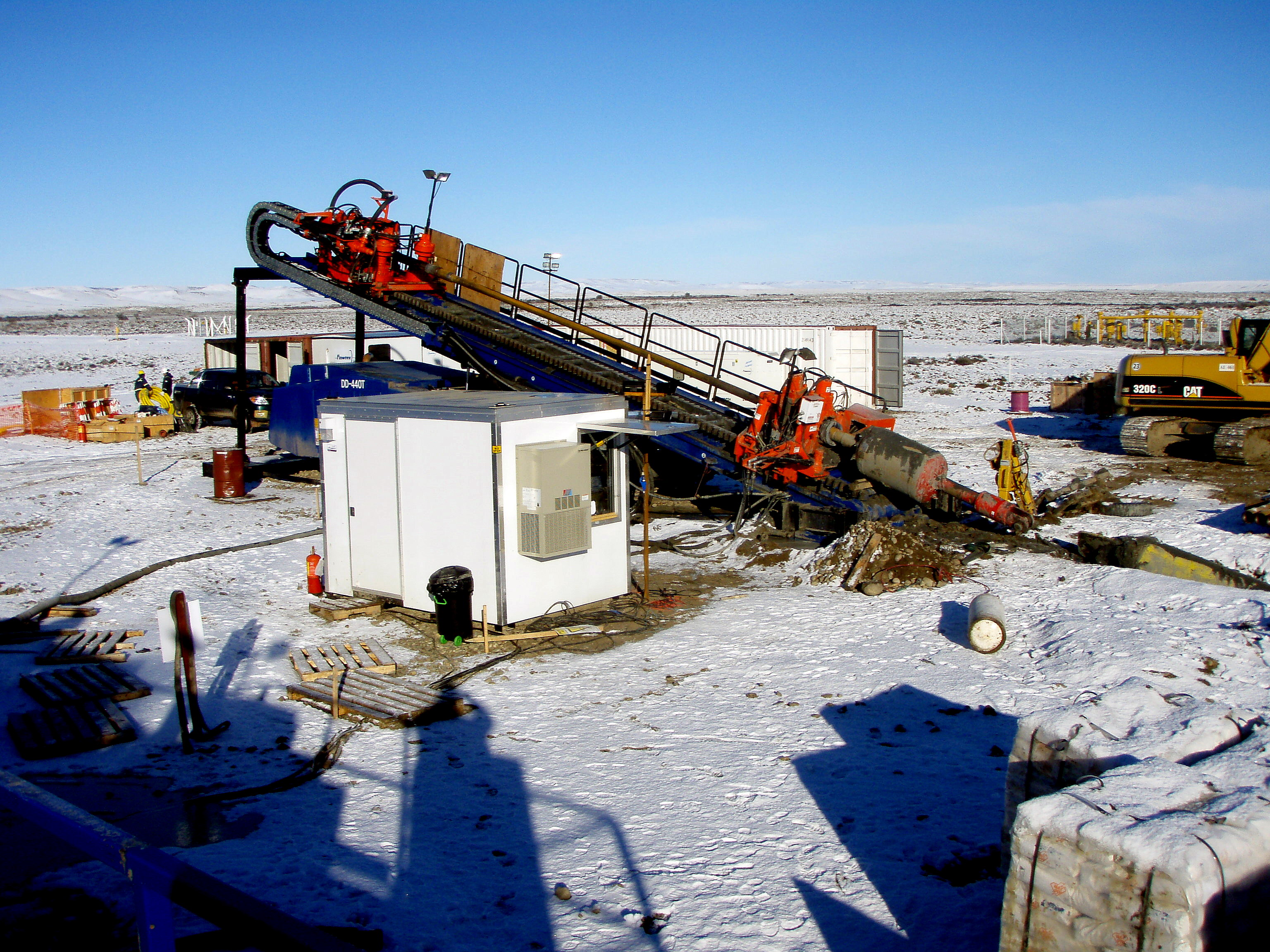
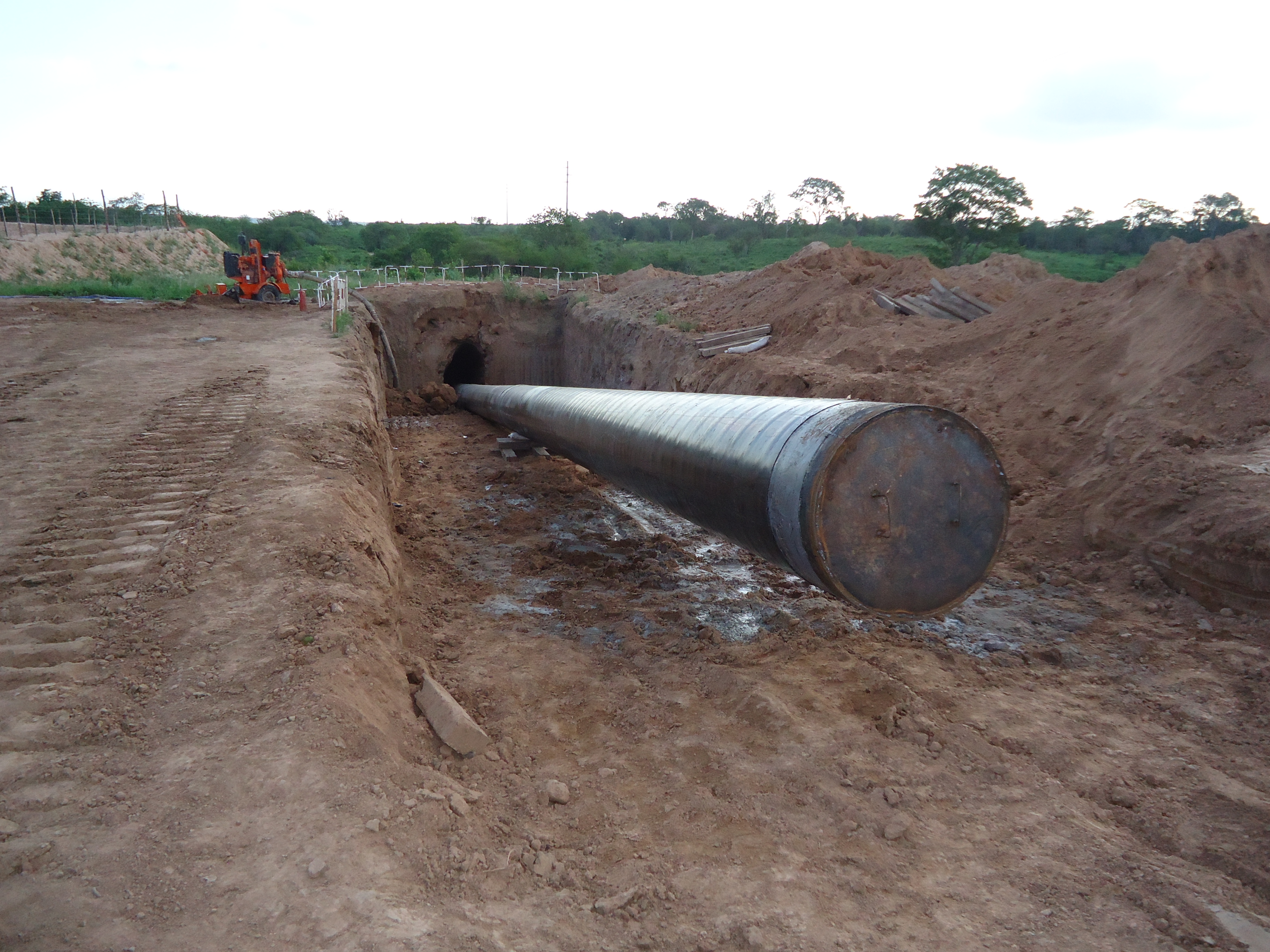
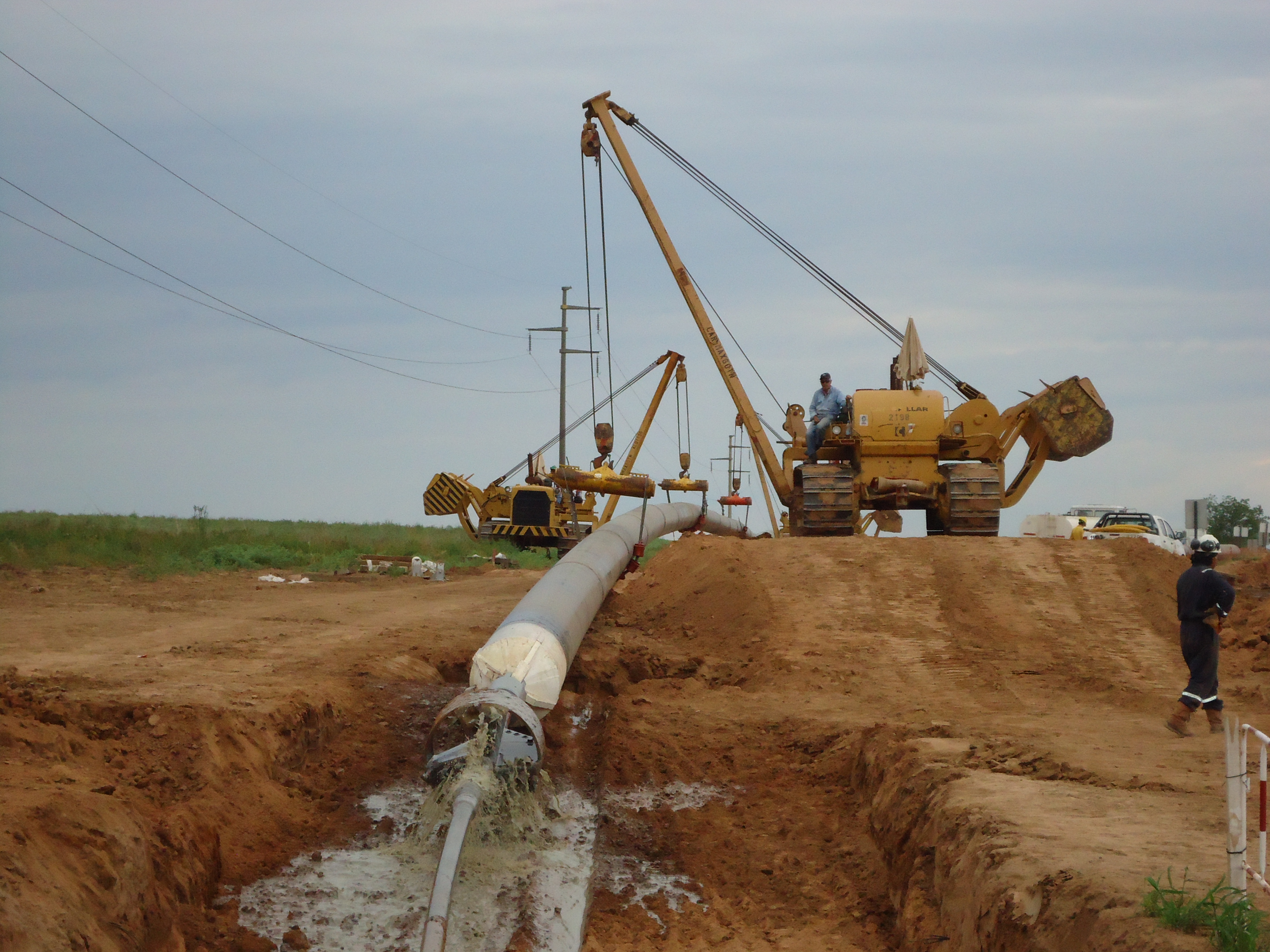
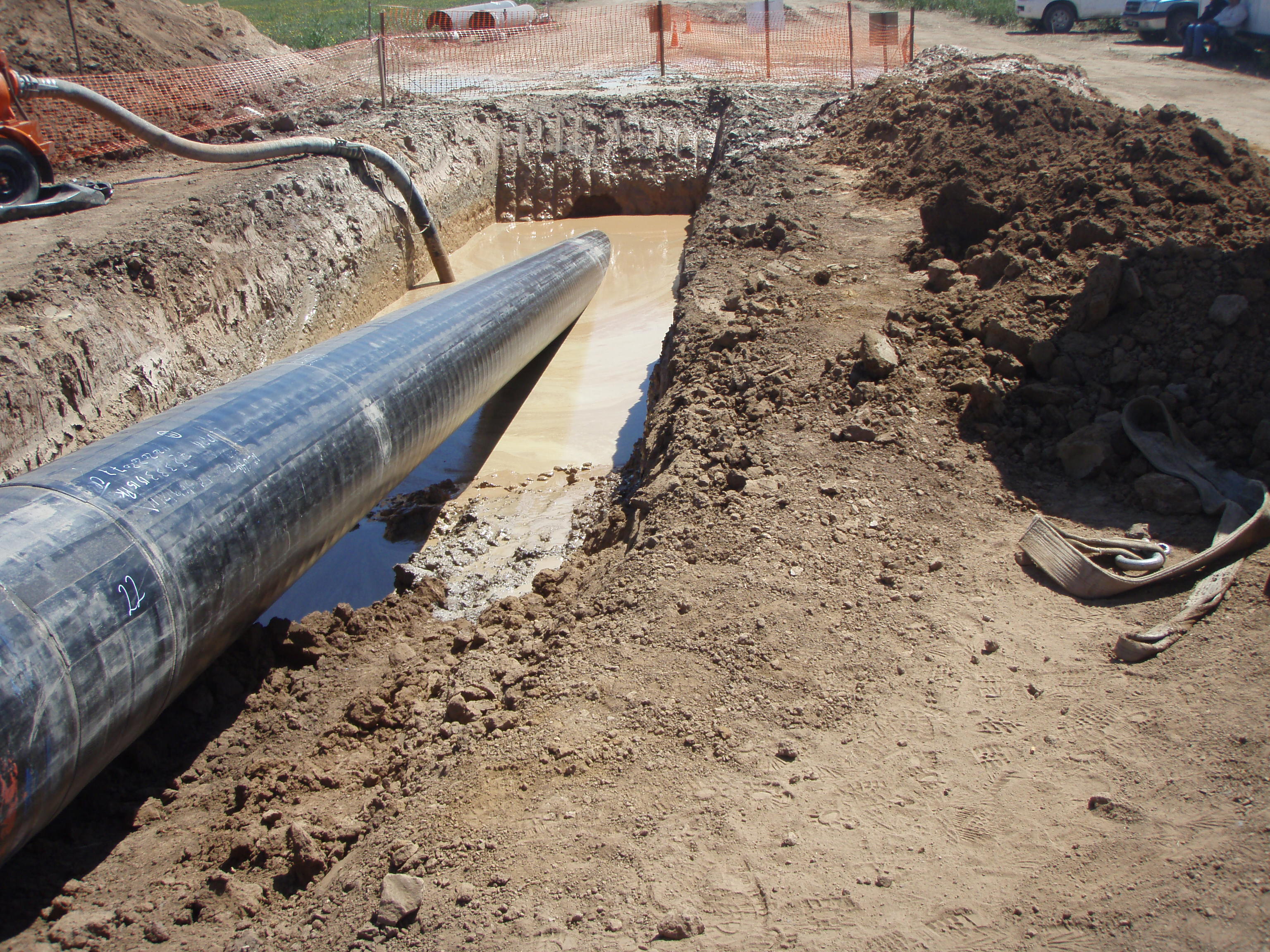
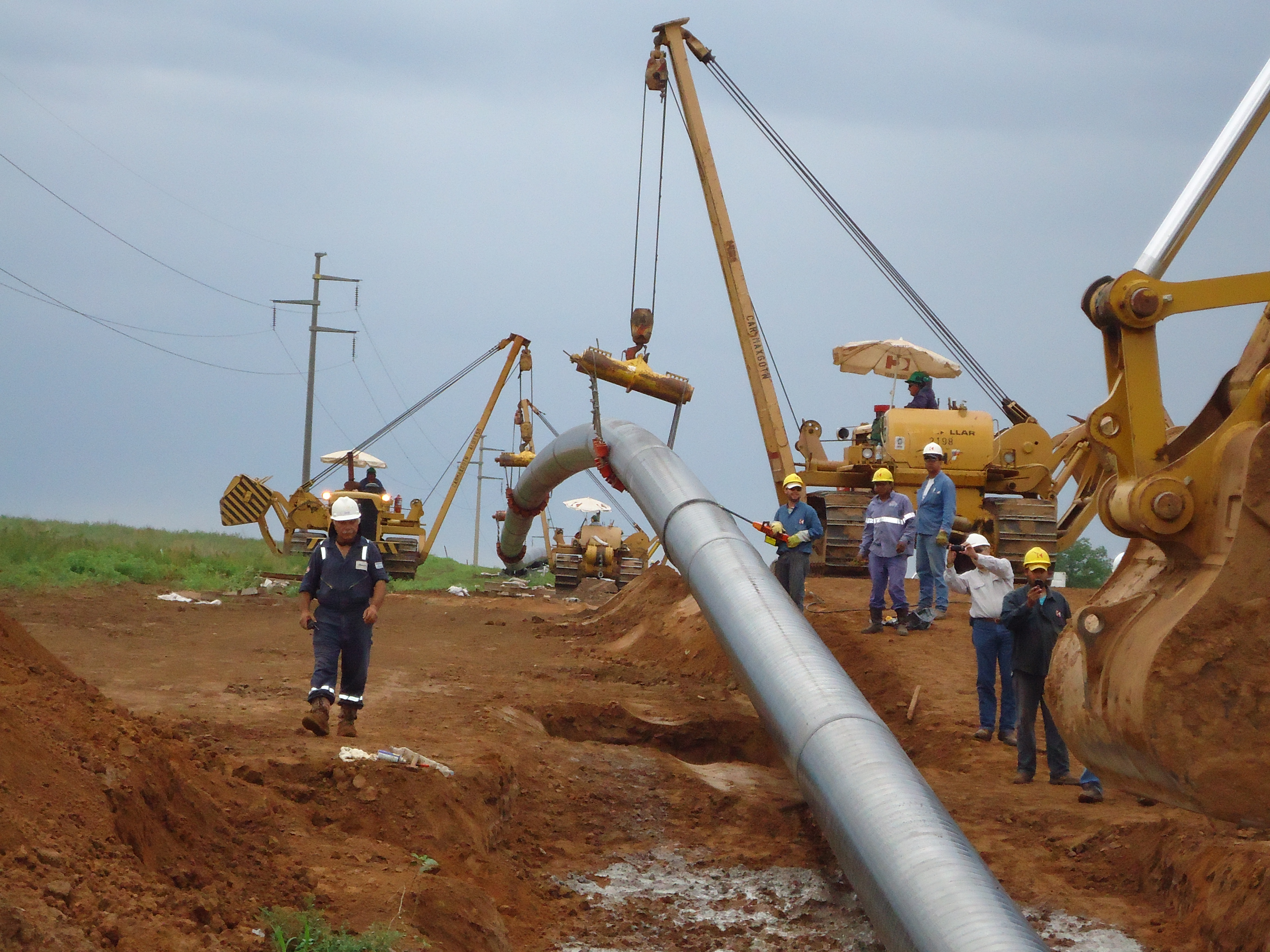
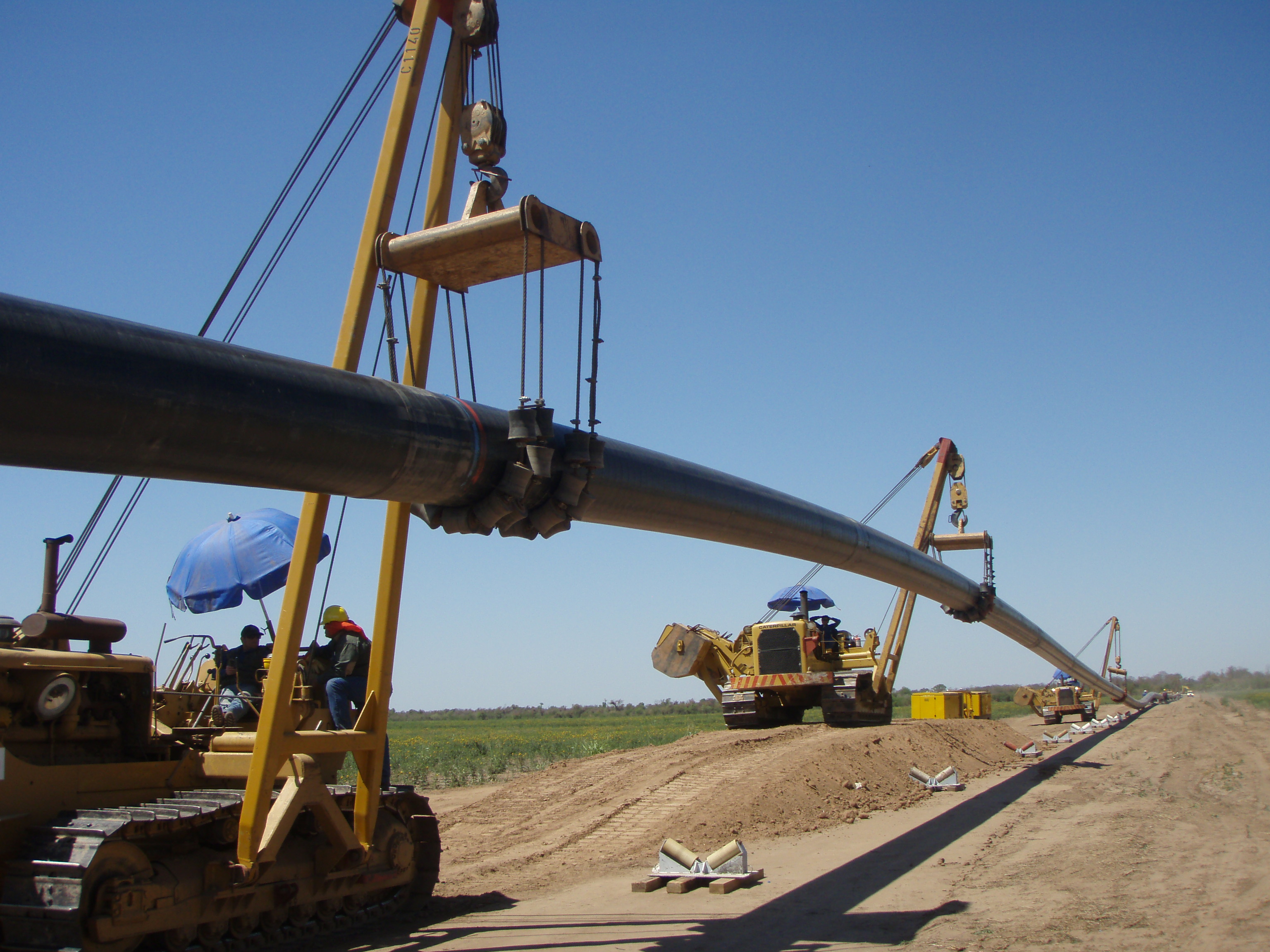
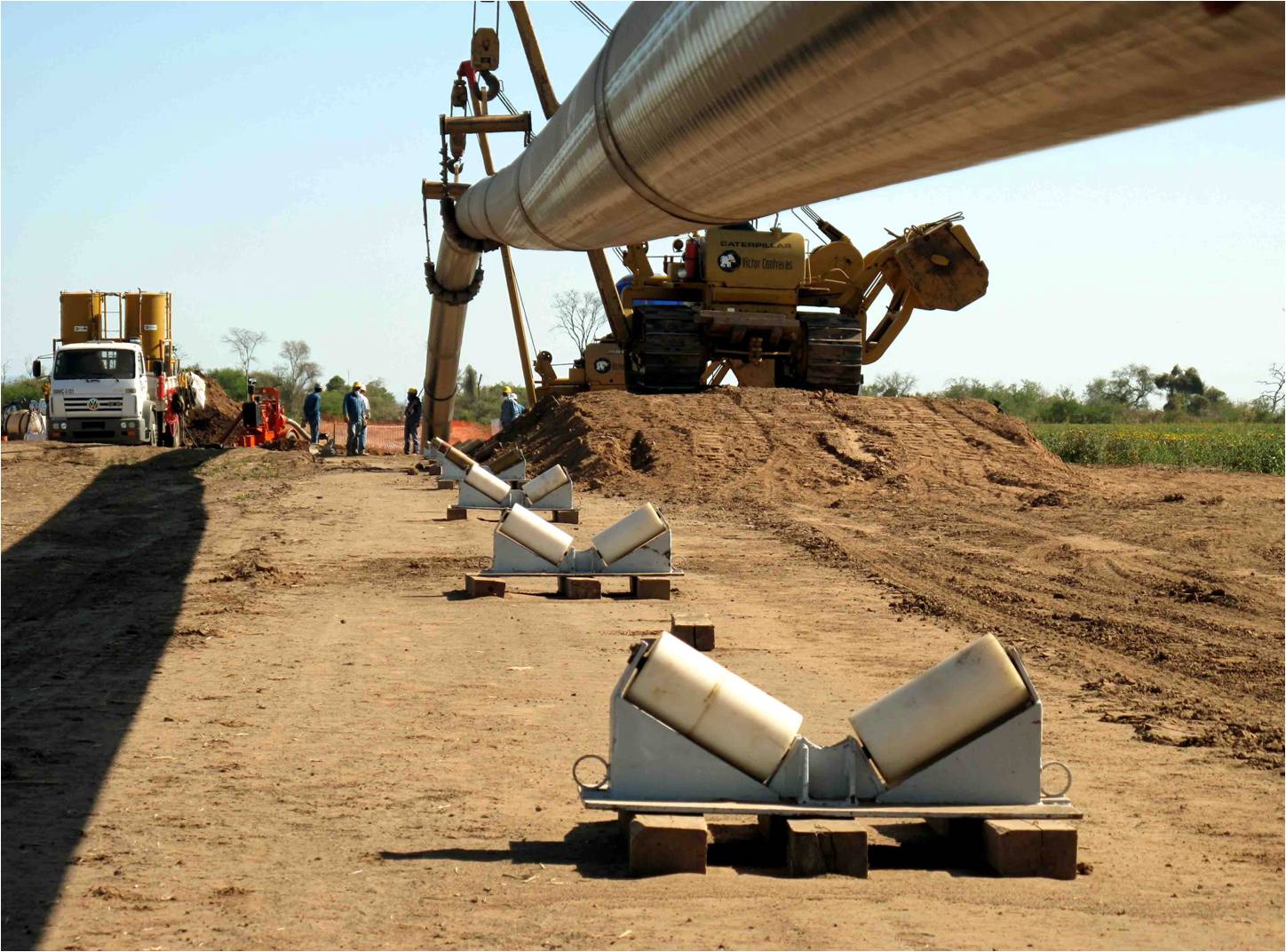
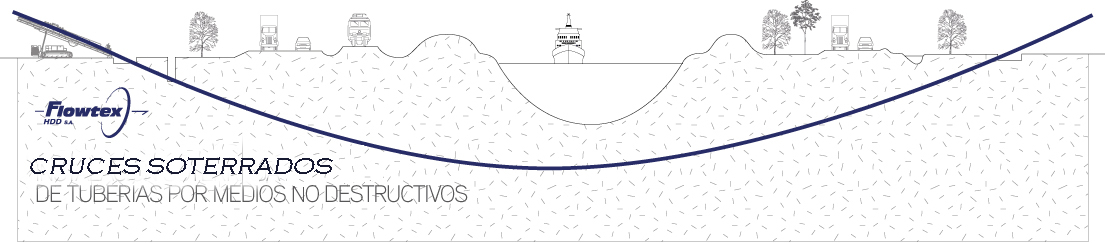
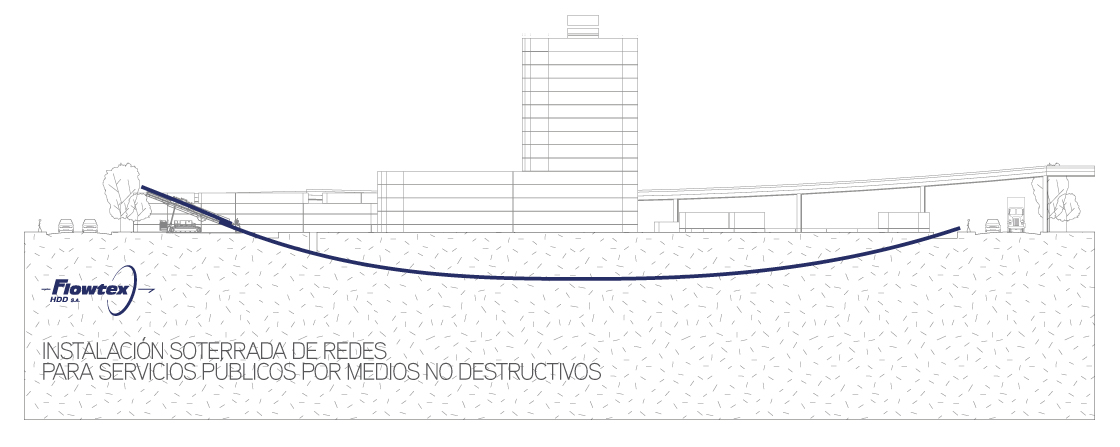
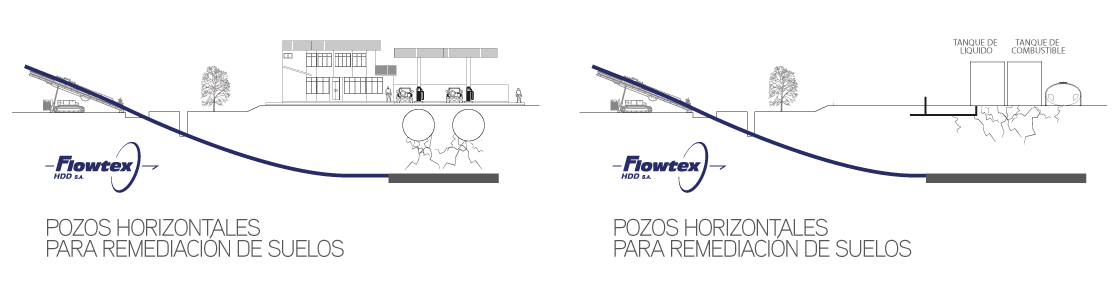
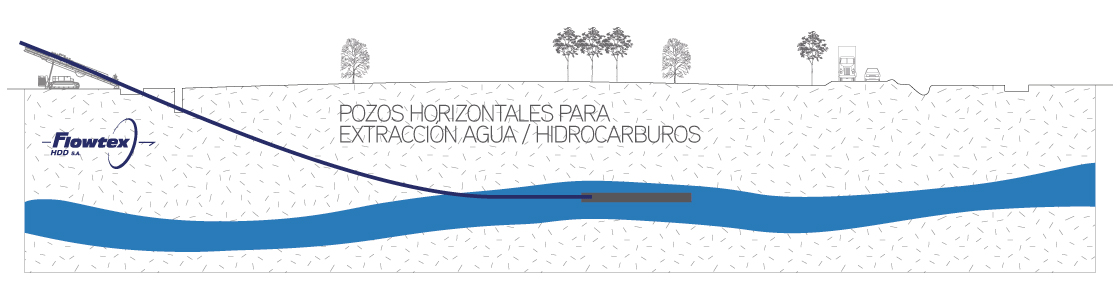
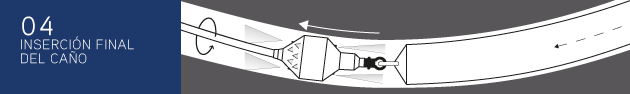
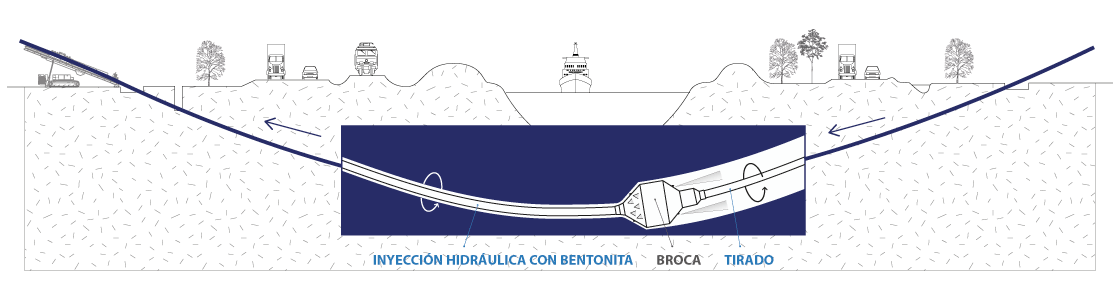
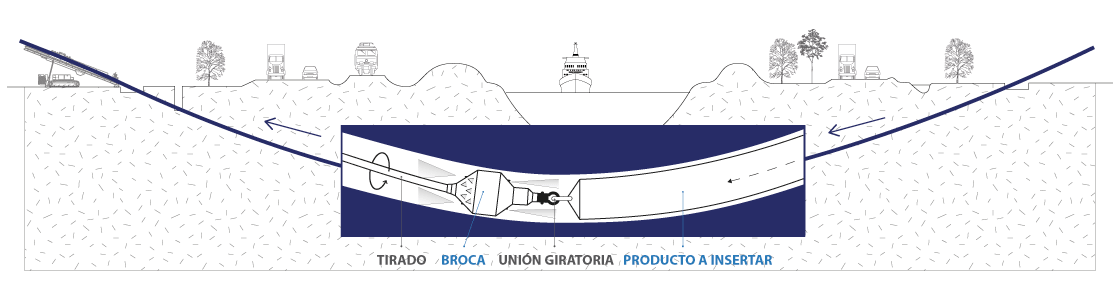
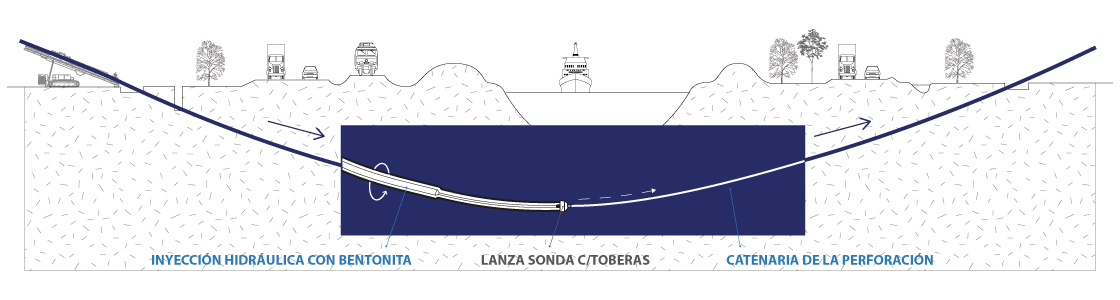
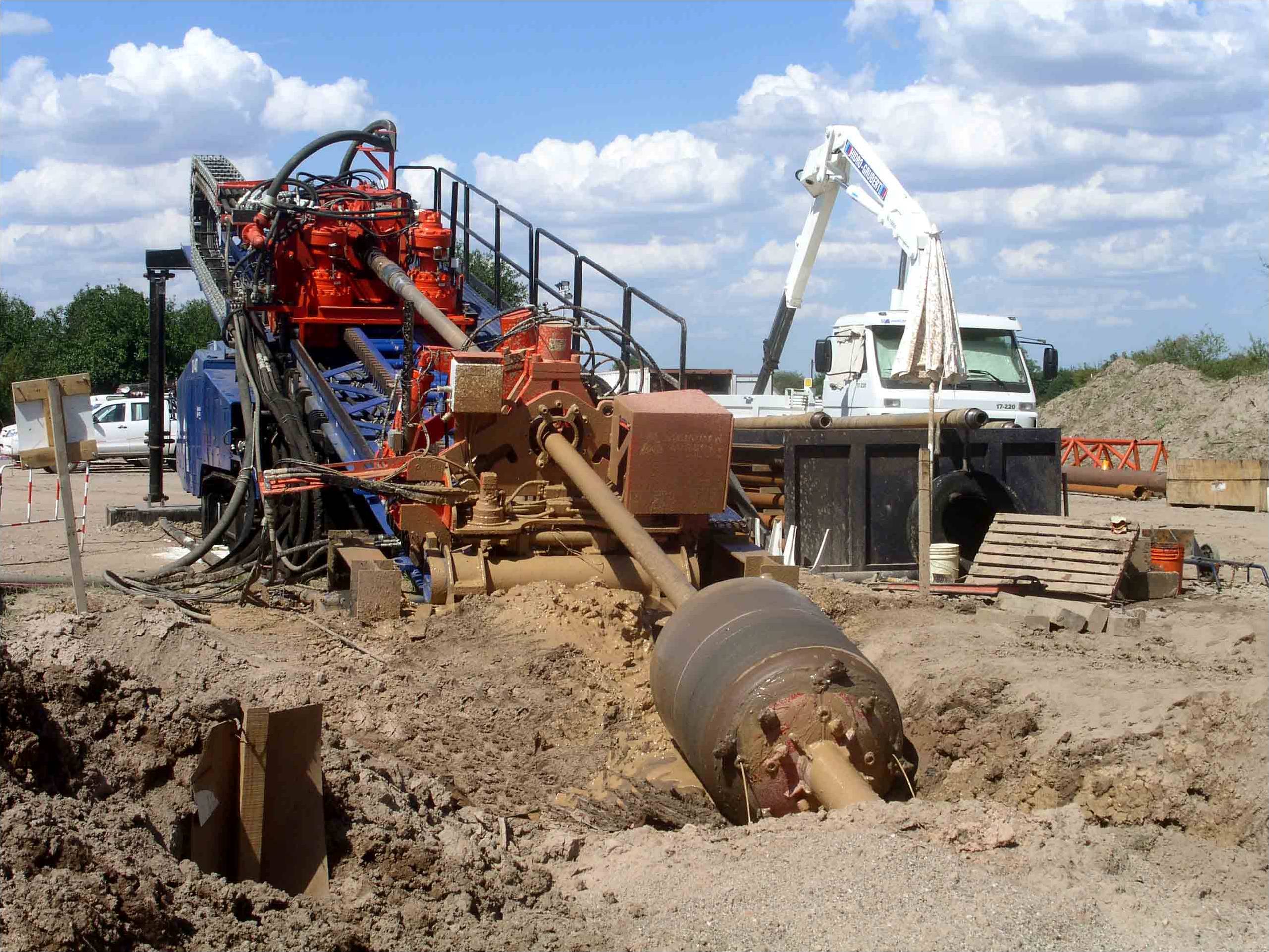
This stage consists in drilling a pilot hole along a pre-designed customer approved drill path. The pilot hole can be drilled from surface to surface, between trenches or pits.
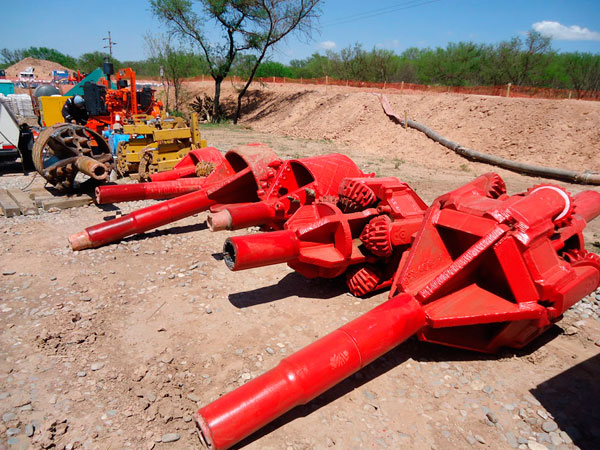
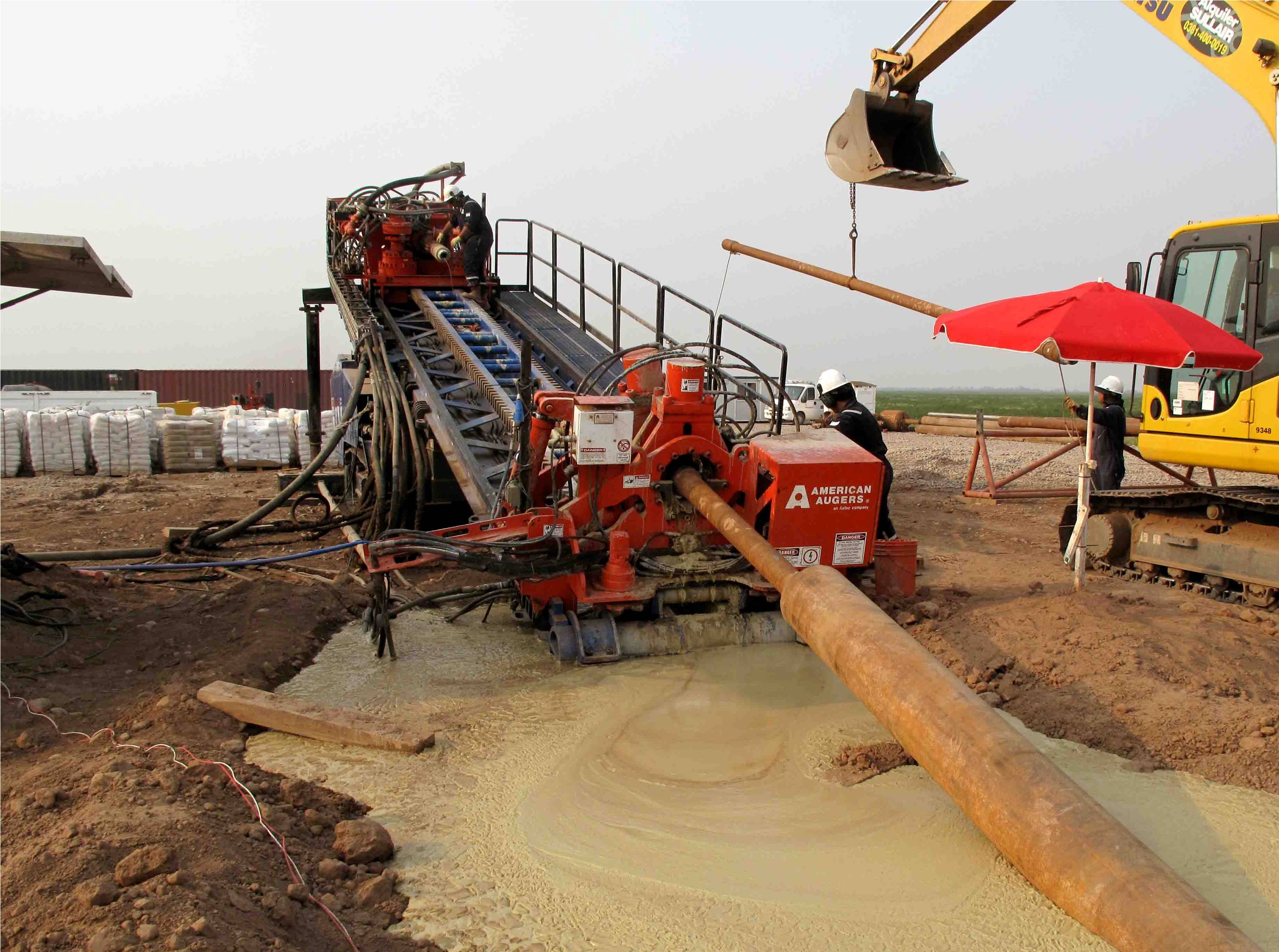
The selection of the tools that make up the drill string which will be used depends fundamentally on the composition of the predominant soil strata to be drilled.

Entry pit

Installation of casing during pilot hole drilling
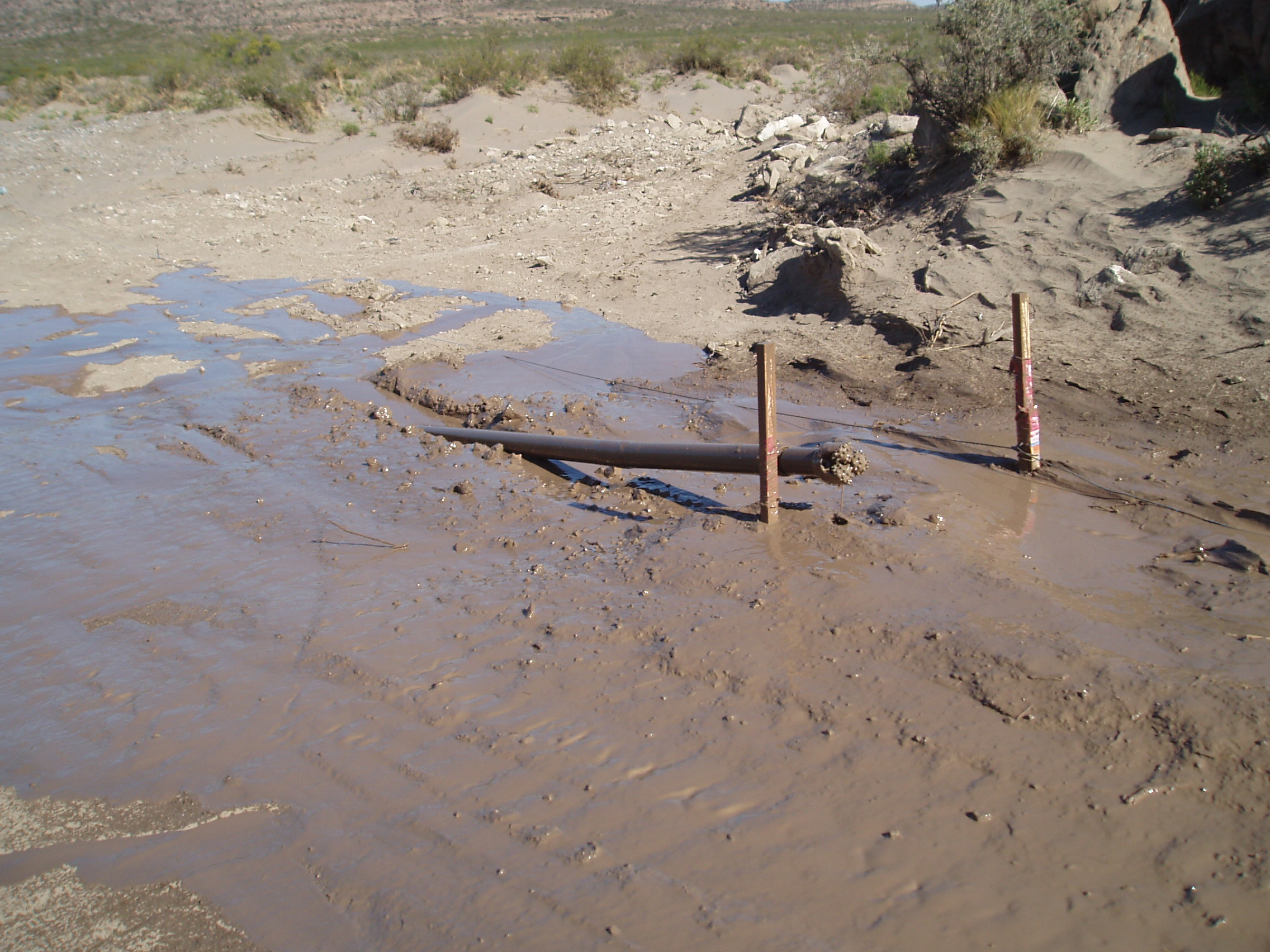

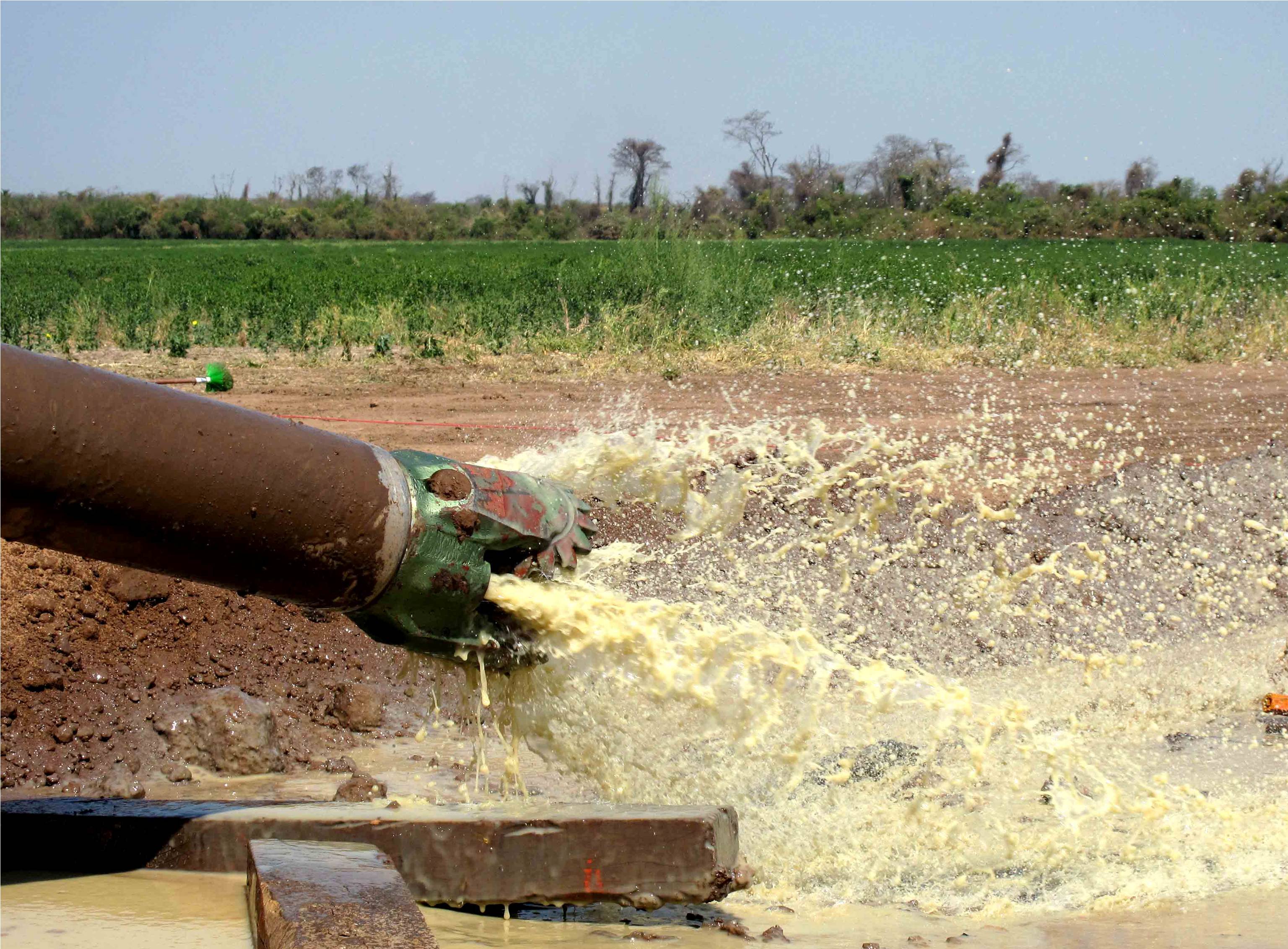
Pilot hole exit
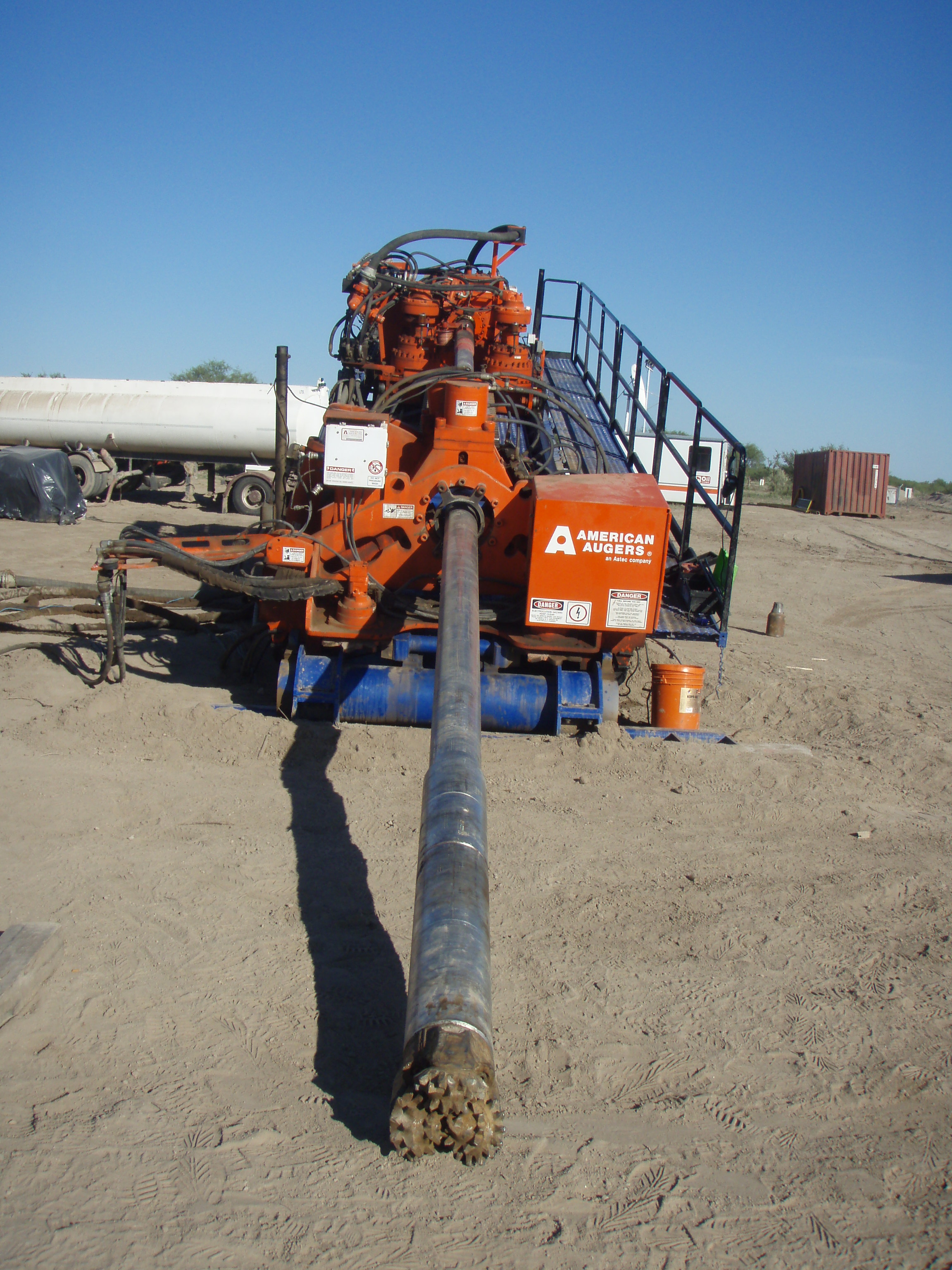

Down hole assembly including non mag section and bent sub
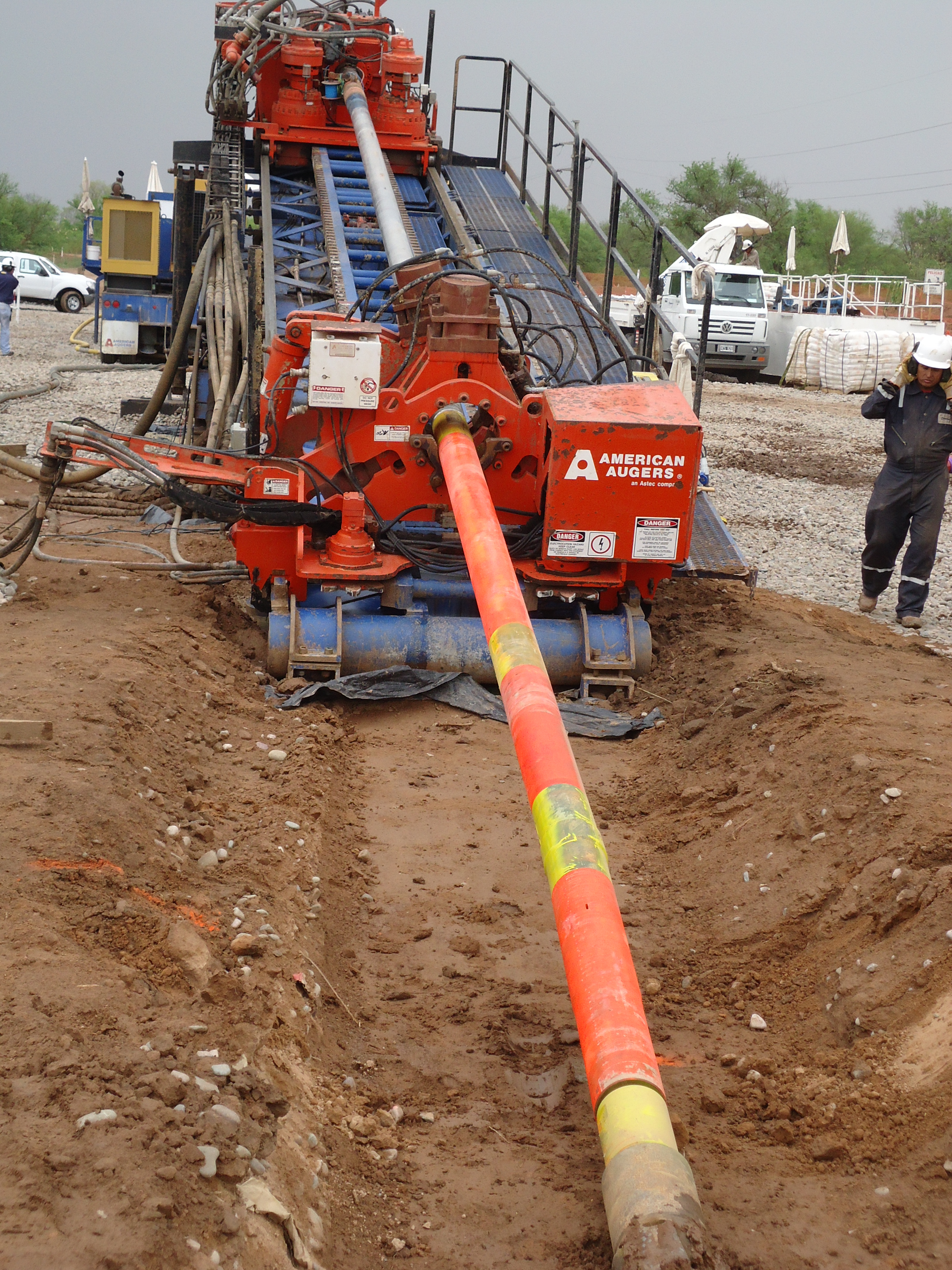

Downhole mud motor
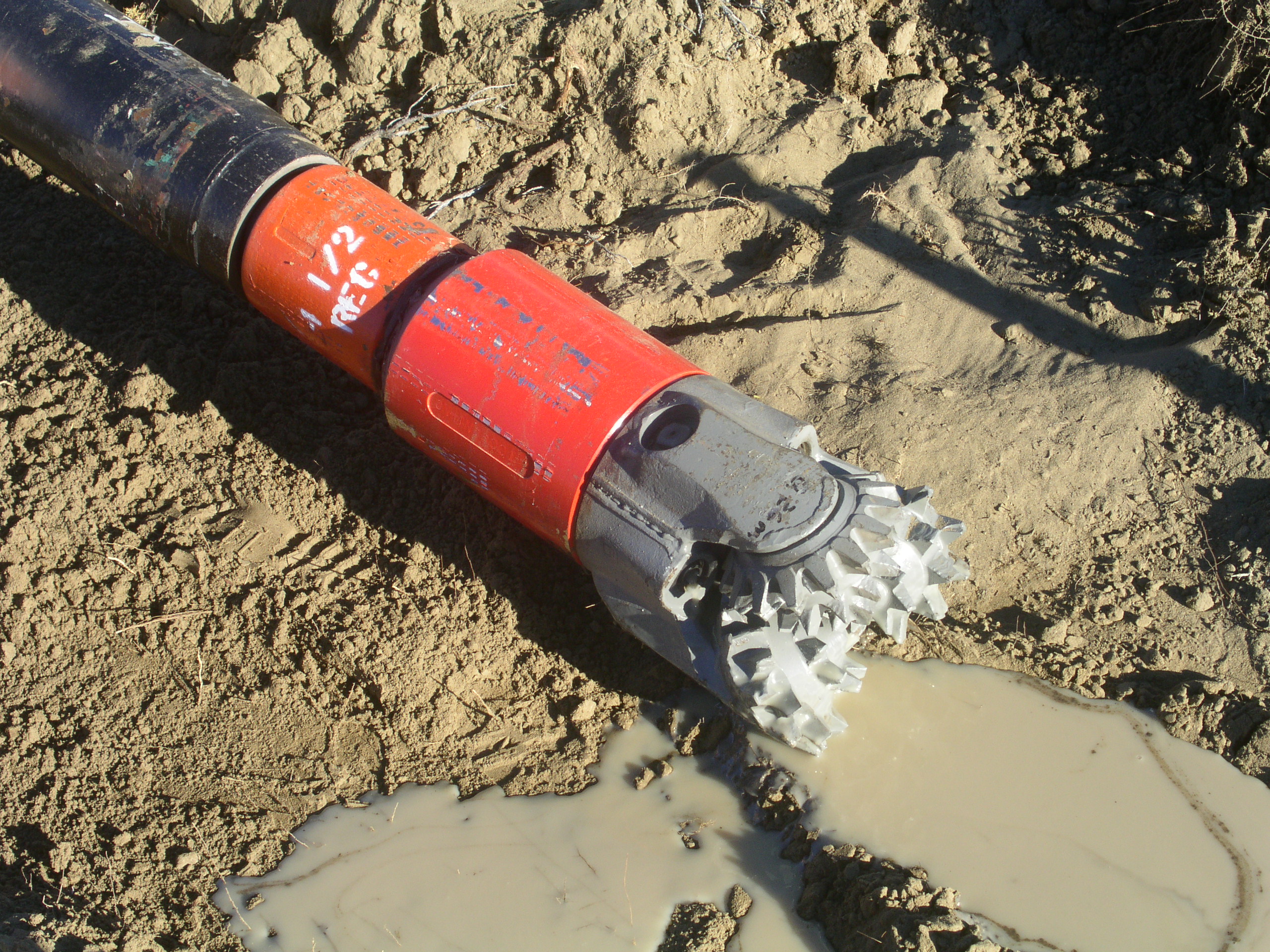

Drilling bit, tricone bit

Duck bill Bit with hydraulic injection
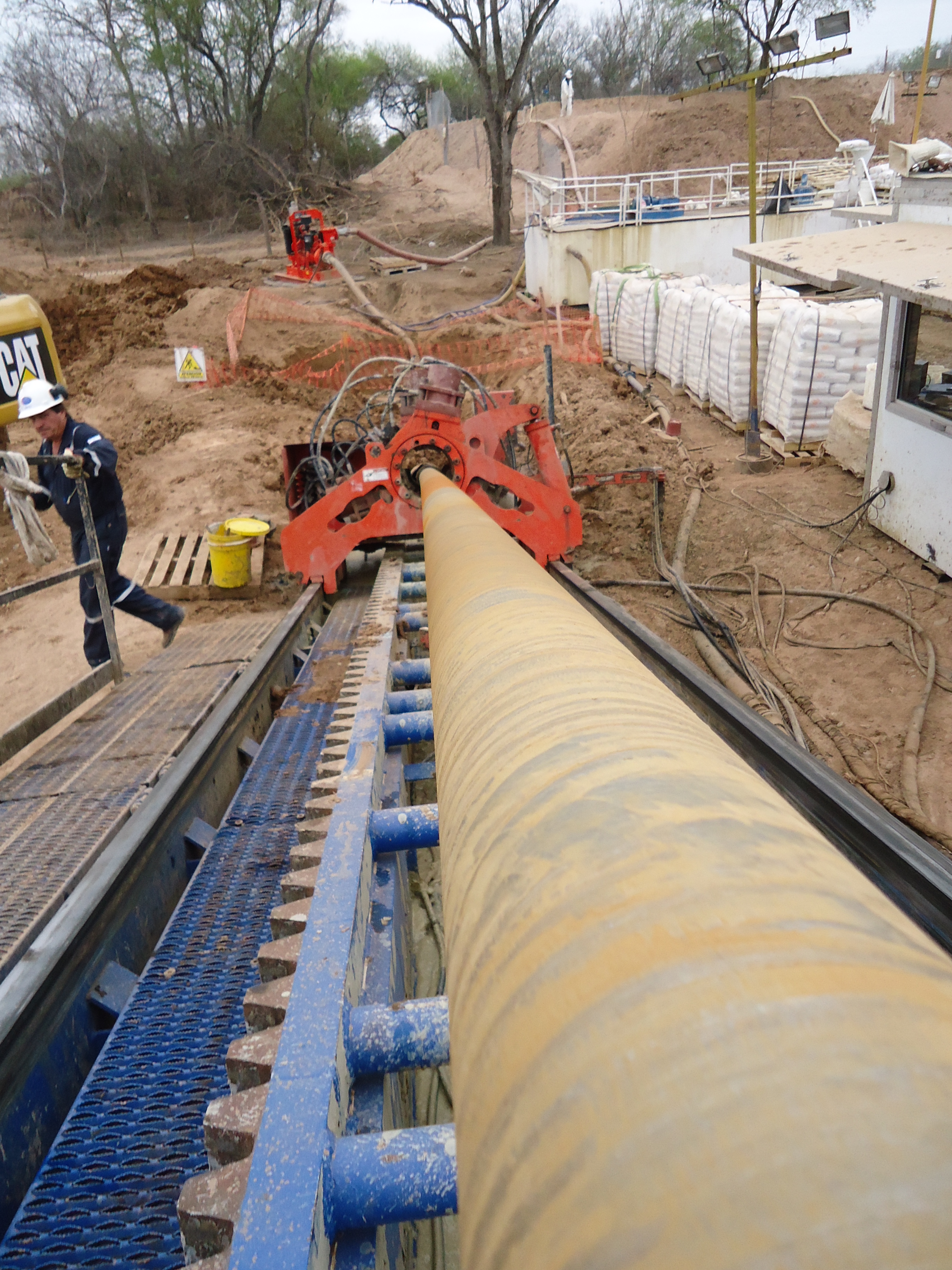

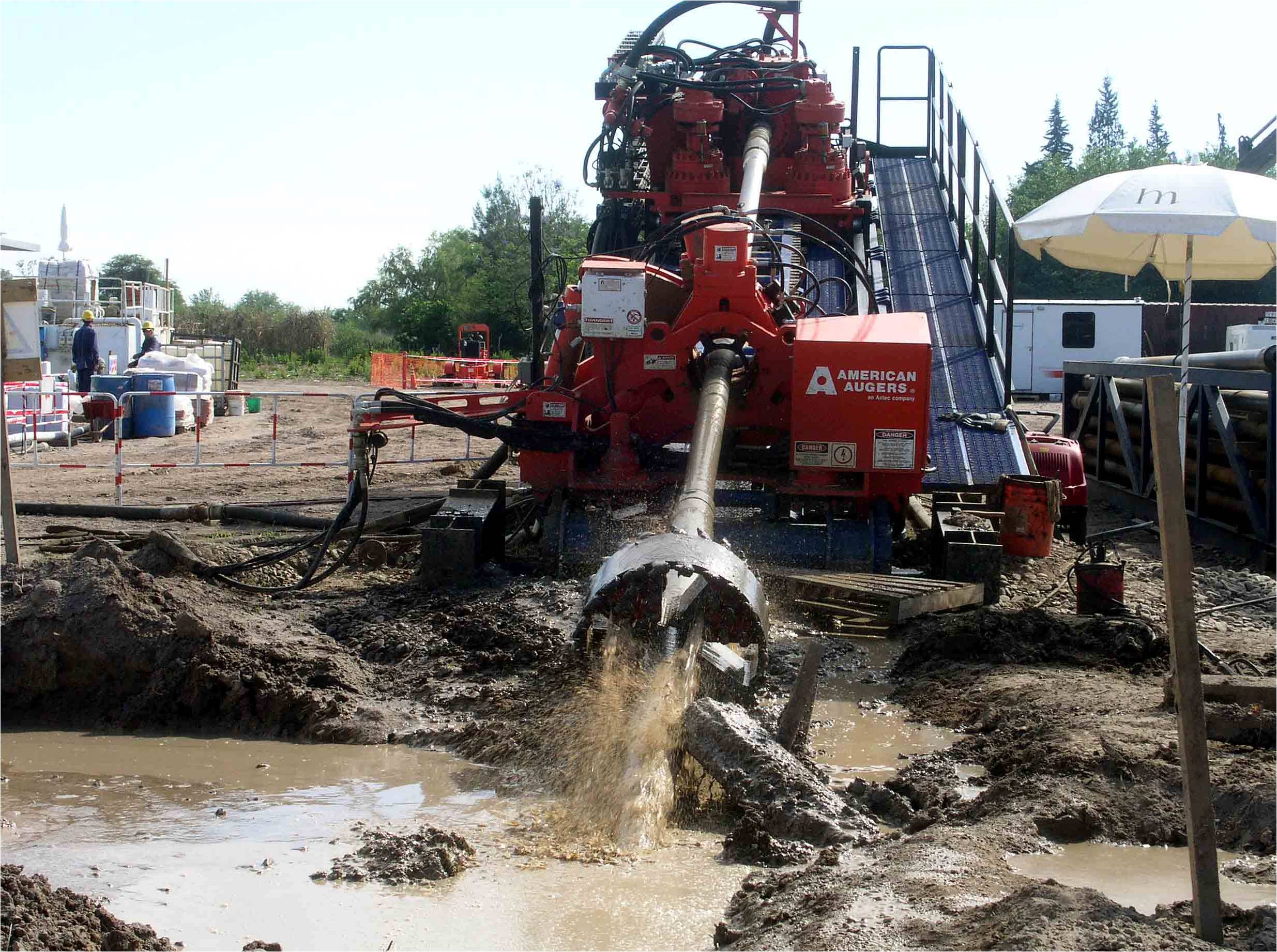
Drilling ramp

Exit swabbing
- PRECISION
- SPEED
- RELIABILITY
TRACKING/SURVEYING
The drilling tool must be guided along its underground path and to that end three different tracking methods are used:
1.- Tracking with walkover system

Repeater
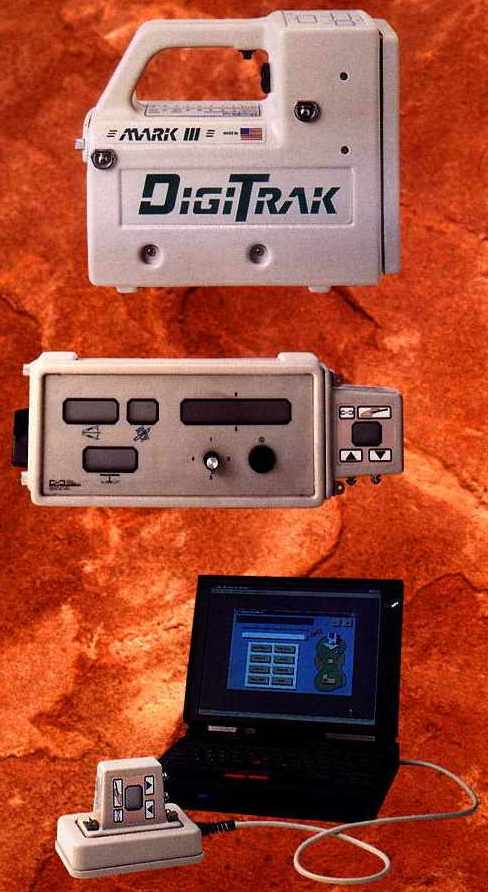

Receiver
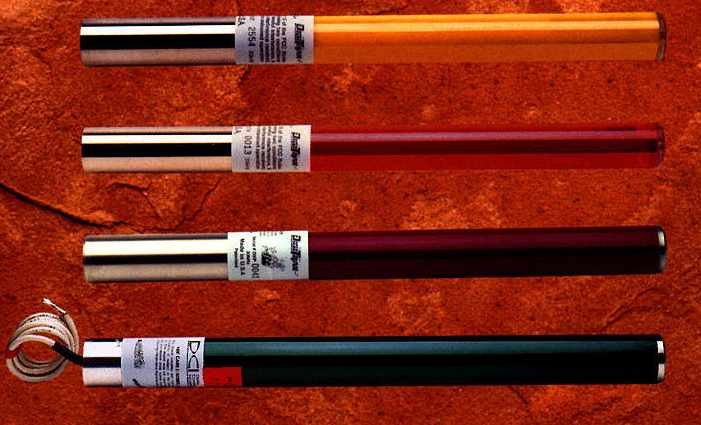

Probe emitting radio frequency signals
2.- Electromagnetic wire line tracking
In this system the probe emits signals corresponding to its inclination, dial position and magnetic azimuth. These signals are transmitted by means of electronic impulses which travel through a cable threaded through the drill string to the drillers’ cabin. Here they are decoded within an interface which feeds the computer and by means of a program then shows the location of the probe.
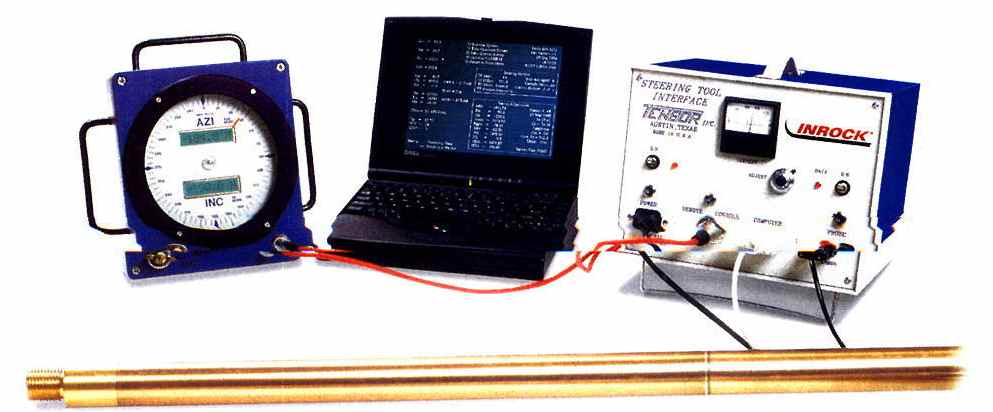

Surveyor with computers
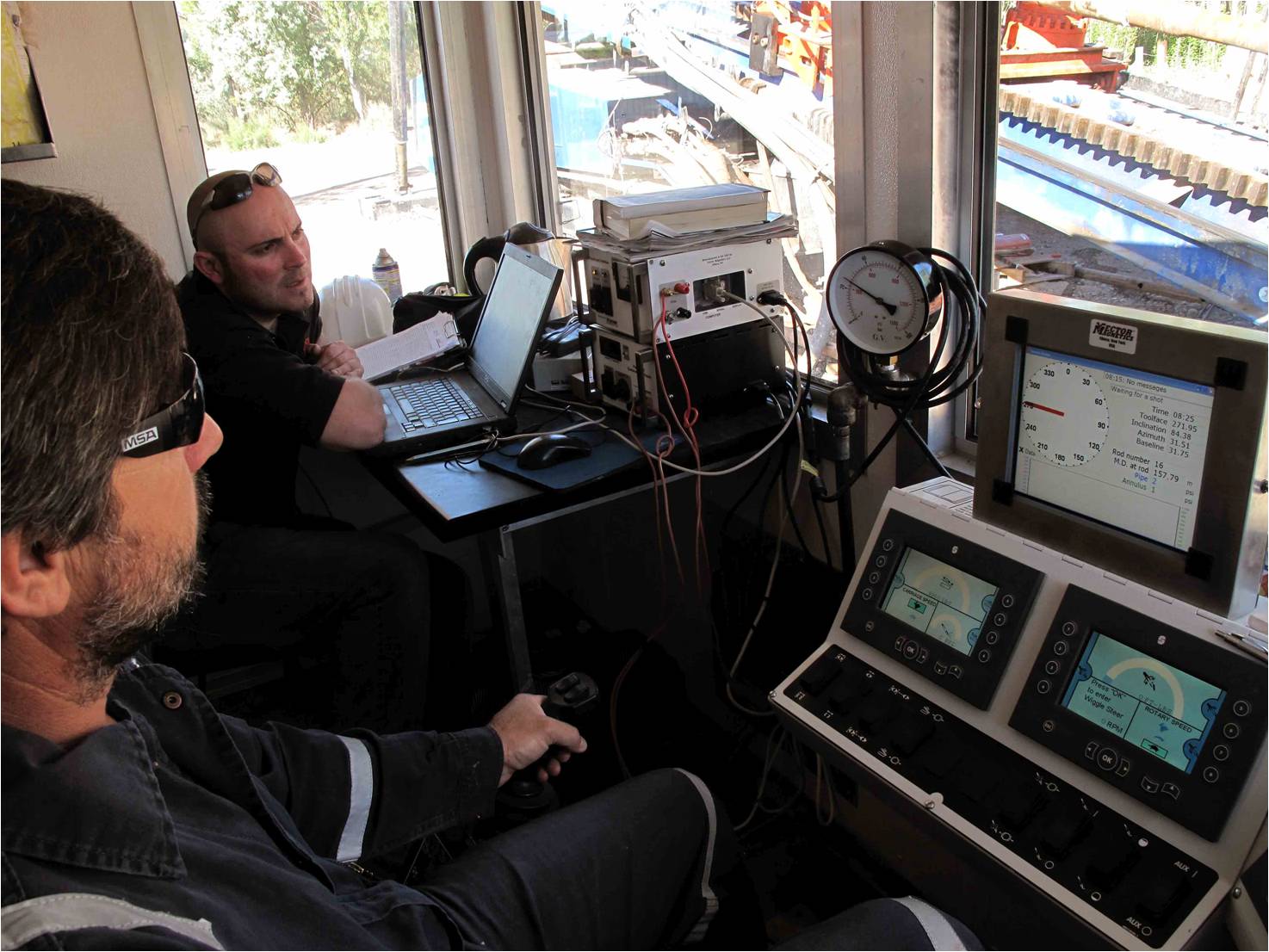

Control screens- Driller
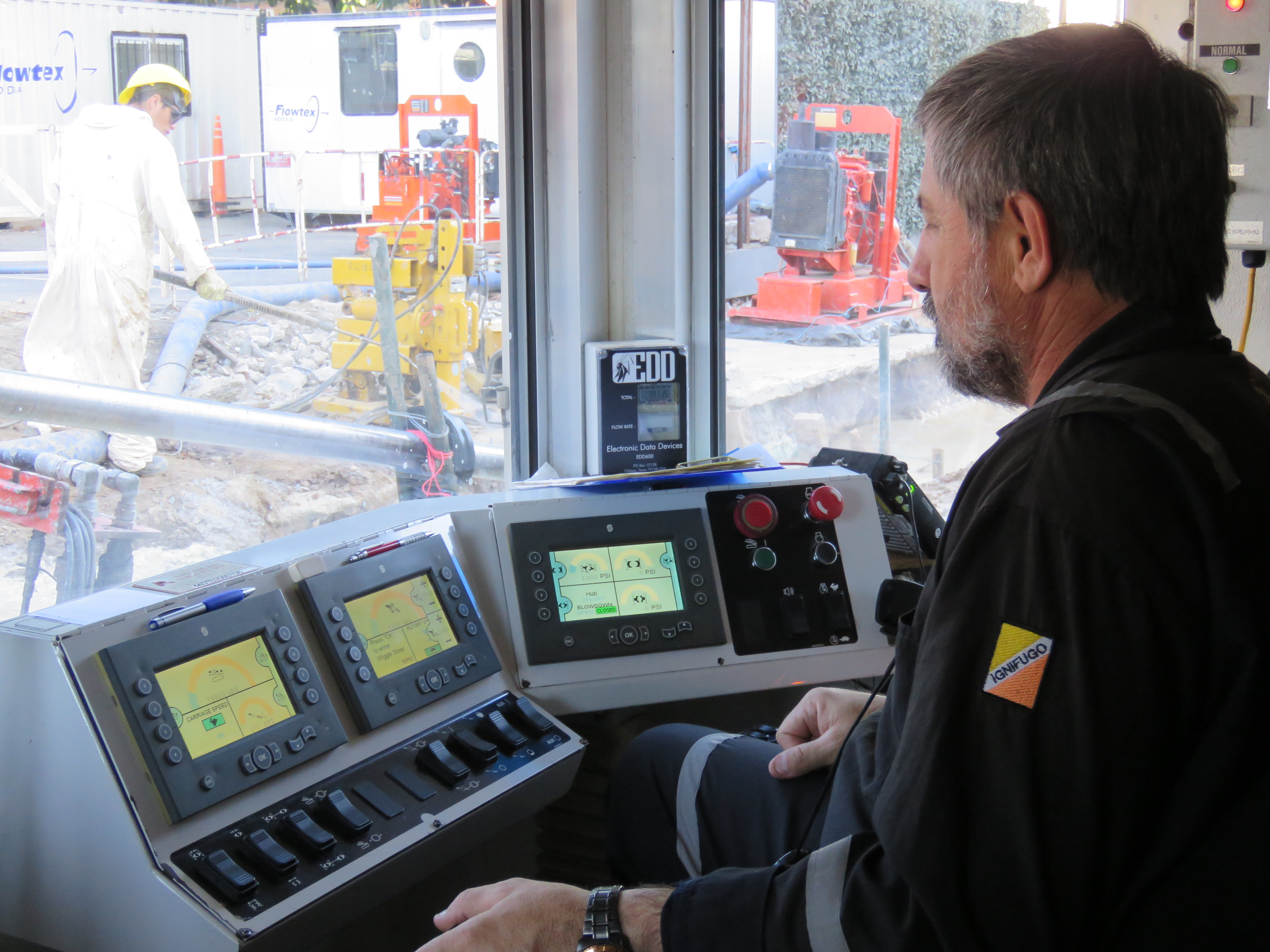

Machine Screens Controller
Magnetic grid or solenoid verification system
So as to achieve greater control of the drill path, electromagnetic guidance systems are linked with the layout of an electrified coil on ground surface. This coil creates an independent magnetic field which allows for a better control of the drill path depth and advance by means of triangulation.
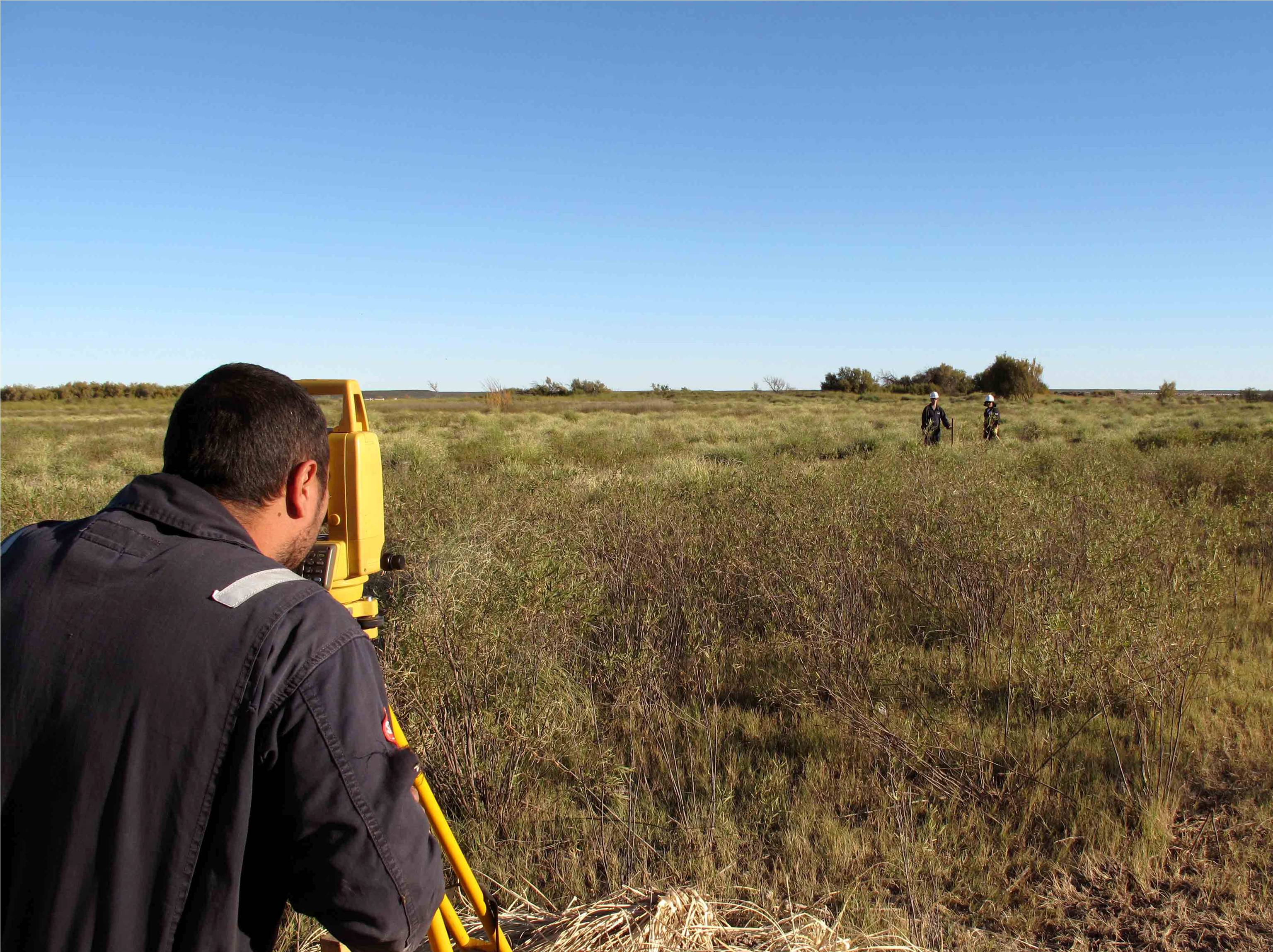

Surveying
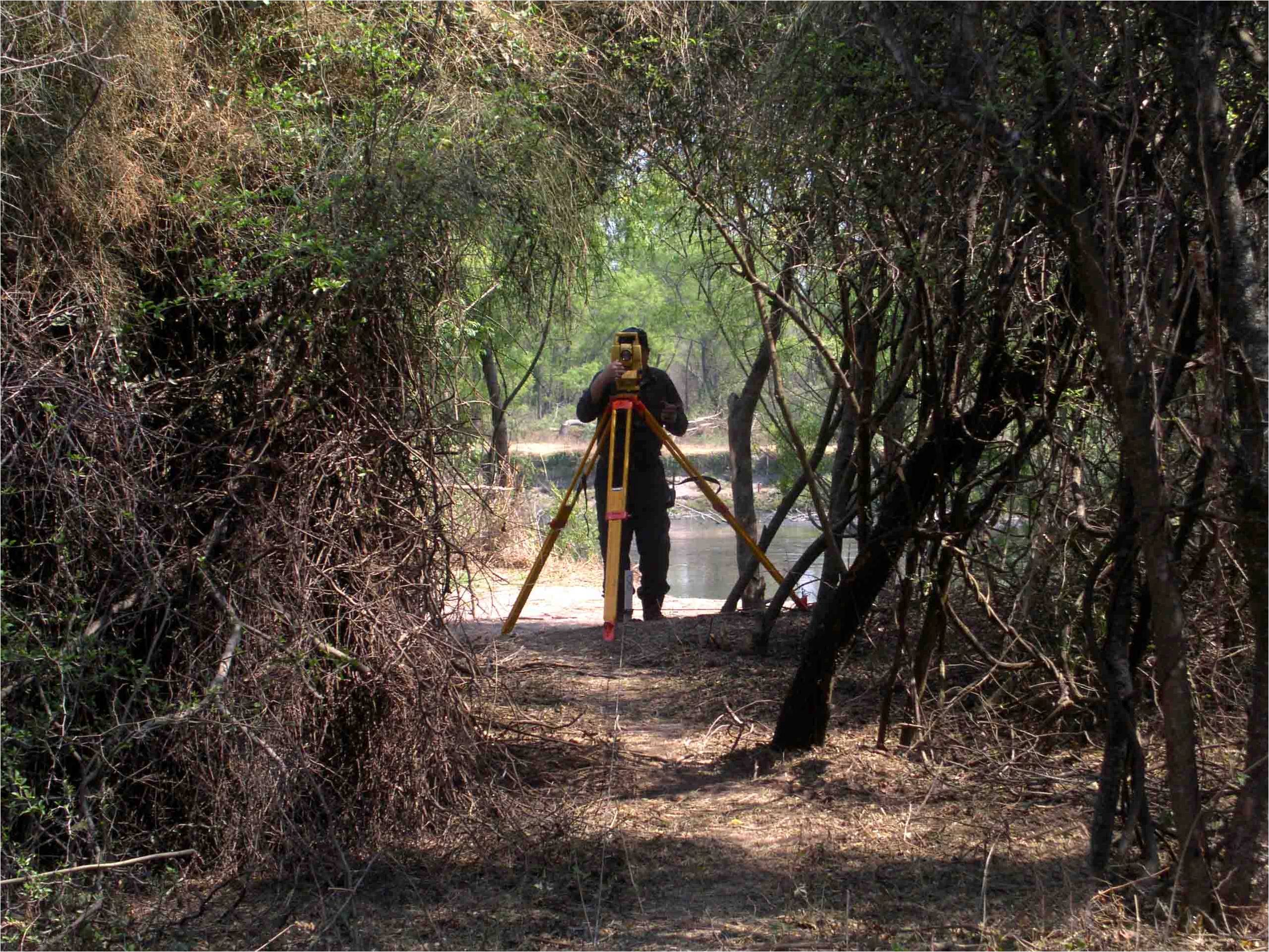

Cable layout
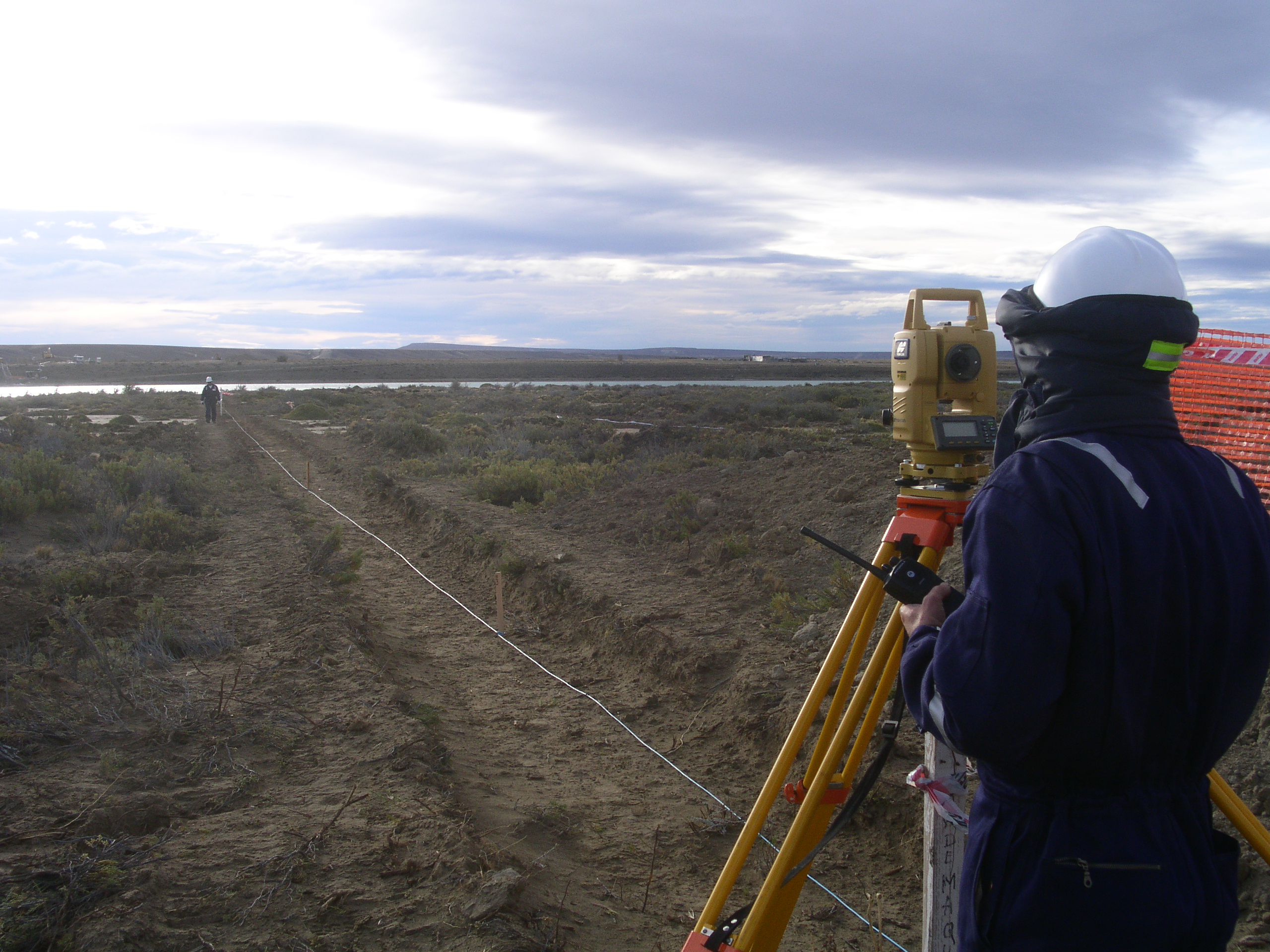

Control with theodolite
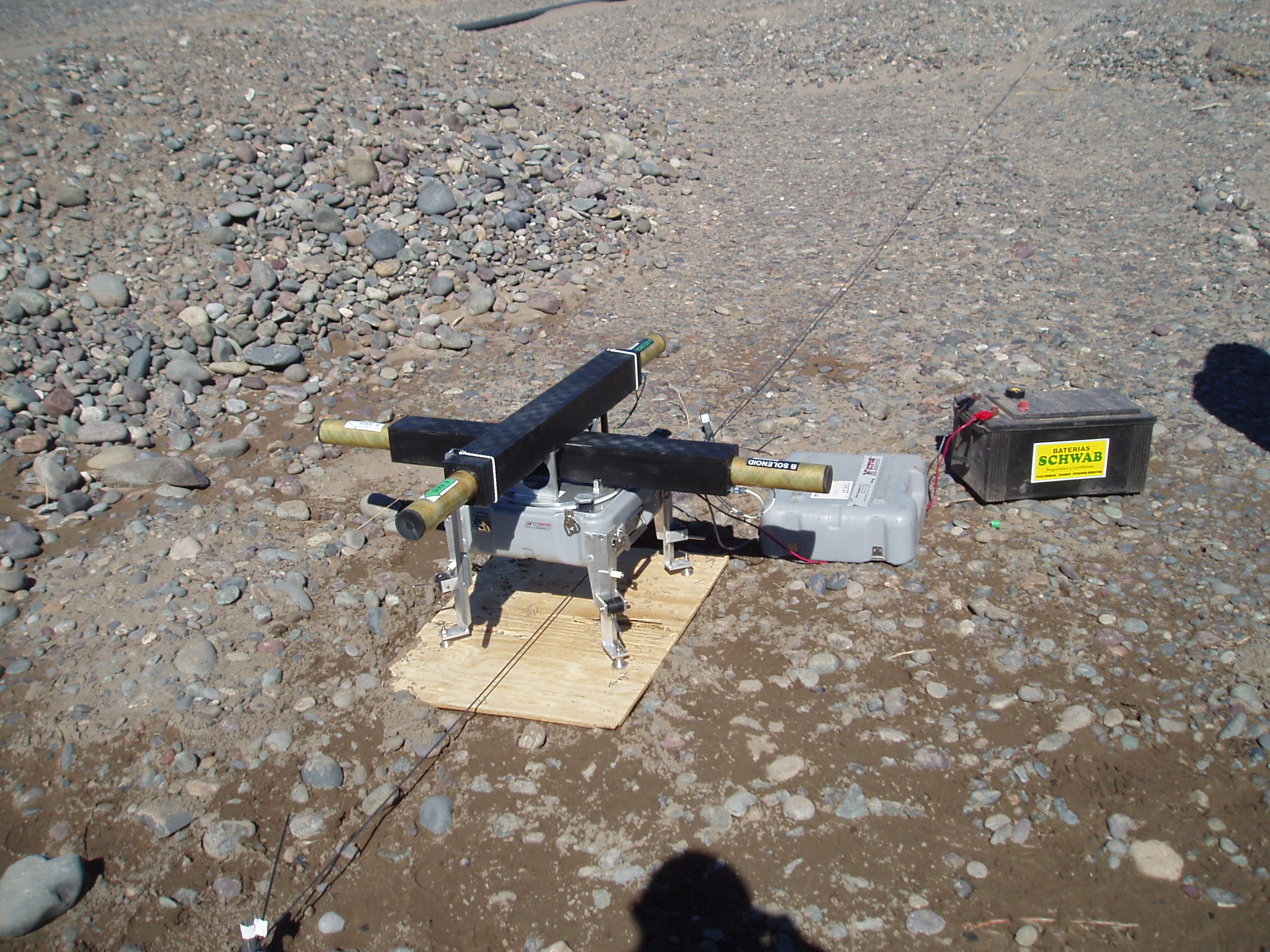

Solenoid
Tracking system with Gyrocompass
A gyrocompass is a nonmagnetic compass constructed so as to be able to use the precision of its effect in the guidance of more complex directional drilling. It travels in the probe inside the nonmagnetic housing, and, as do the electromagnetic systems, feeds and connects with computers in the control cabin through cables threaded through the drill pipe string. Even though less frequently used because of its greater operational complexity, in combination with accelerometers, it provides an extremely accurate tracking tool, possessing three significant advantages over the magnetometers:
- it finds the true north in accordance with the Earth’s rotation, which is different and more useful than the magnetic north,
- it is not affected by ferromagnetic materials, such as rocks of volcanic origin or neighboring metallic elements or pipelines, which change the magnetic field,
- it allows precise tracking below large water surfaces